Fighting Disinformation in Modern Conflicts

Introduction:
The current repetition of interest in disinformation is not because the idea is innovative, but rather there is a growing consent that the digital revolution has greatly enhanced public vulnerability to manipulation by information, therefore, action needs to be taken to counter it. The related concept of propaganda has been around far longer, but many people see this as a means of driving engagement and mobilization for social or political change, rather than simply to mislead. The relatively new term ‘fake news’ covers a far wider range of content, often with financial motivations rather than political ones. Disinformation is the new tactical method in modern conflicts to create an environment where institutions can justify their violence, Governments can build their narratives and non-state actors preach their political ideology. Misinformation and fake news are new bombshells which are lunched from social platforms that leave impact on the human minds in large numbers. Modern militaries and actors in the conflict called this Hybrid warfare that is more effective and impactful than the actual military operations. Psychological operations by using the power of social media have become the part of military strategies in the realm of defense policies.
 Disinformation Impact on Human lives:
Disinformation Impact on Human lives:
According to the World Risk Poll, “fake news” topped the list of concerns for internet users in 2022. Military and civilian actors alike have made gainful use of disinformation in order to control the narrative regarding the conflict. The deep civil disintegration individuals of conflict settings amplifies the effect of such disinformation by creating echo chambers that intensify confirmation bias and accelerate the uncritical sharing of inaccurate events or reports. Practically, conflict-affected persons may be especially vulnerable to the ill effects of disinformation due to their frantic living conditions, elevated exposure to violence and lack of access to trustworthy sources of information. Compounding the potential for harm is the fact that conflict environments have proven especially fertile incubators for disinformation, as evident by its recent flourishing nature in Israel and Palestine, Libya, South Sudan, Syria, Ukraine and Yemen.
Russia-Ukraine Conflict:
In the recent confrontation between Russia and Ukraine, CNN reported that, “The Russian assault on Ukraine is not just an unprovoked attack on a sovereign nation that is producing horrific destruction and civilian torment. It is also the biggest war of the modern misinformation era”, some scholars argued that, Russia’s misinformation offensive impedes diplomatic efforts to end the war. Russian state media has portrayed Russian’s as victims of the war and covered the invasion as an attempt to liberate the Ukrainian population even as bombs and missiles rain down on civilians. On diplomatic forum, Russians has been denying the existence of war. Russian Foreign Minister Sergey Lavrov claimed with a straight face after talks with his Ukrainian counterpart in Turkey which, not surprisingly failed, that “Russia did not attack Ukraine”. It is an approach that has multiple payoffs for Moscow. It can be used as cover for atrocities and potential war crimes like the attack on the maternity hospital. Misinformation also plays into the Kremlin’s narrative about the nature of the war, that it is the victim, which is served up to Russians on state media networks. The Russian claims might be absurd but they also find an audience among conspiracy theorists on social media and can be used by propagandists, even in Western countries to cast doubt on the credibility of leaders building a united front against Moscow.
The disinformation fight:
The Oversight Board was created in 2020 by Zuckerberg but it is an independent body made up of former world leaders, activists and top lawyers to make decisions on the most significant content moderation challenges on Facebook and Instagram. Disinformation and misinformation are major challenges on these platforms and have always been important issues for the board because of the wide use of these social applications. Although social media companies have a big impact on people’s lives but the disinformation fight cannot be solved by Big Tech alone. United States and UN should step out to mitigate these challenges on domestic level as well as on international platforms. In Pakistan, Government had passed Prevention of Electronic Crimes Act (PECA), through ordinance to handle fake news and disinformation on social media. International Humanitarian Law (IHL) takes a remarkably lenient approach to such misinformation actions and stratagems with one exception. Combatants may not resort to perfidy, defined in Article 37 of Additional Protocol to the Geneva Conventions as “inviting the confidence of an adversary to lead him to believe that he is entitled to, or is obliged to accord, protection under the rules of international law applicable in armed conflict, with intent to betray that confidence”. Belligerents thus may not, for example, disingenuously accept a truce or announce their capitulation, feign injury or illness, or claim civilian or other protected status.
 In the next paragraph of Article 37, however, explicitly permits ruses as “acts which are intended to mislead an adversary or induce a person to act recklessly but which infringe no rule of international law applicable in armed conflict and which are not perfidious”. While this particular provision only pertains to international armed conflicts (IACs), ruses are likewise licensed in non-international armed conflicts under customary international law. But modern applications of misinformation or more accurately, disinformation call into question its reflexive characterization in IHL as a ruse for several reasons. First, while ruses are presented in source materials as being intended to mislead an “enemy” or “adversary”, disinformation campaigns during armed conflict today are instead often oriented primarily towards the civilian population. Under that obligation of IHL, Militaries can mislead their enemies on the battle field, but they cannot misguide or mislead the population in International armed conflicts.
In the next paragraph of Article 37, however, explicitly permits ruses as “acts which are intended to mislead an adversary or induce a person to act recklessly but which infringe no rule of international law applicable in armed conflict and which are not perfidious”. While this particular provision only pertains to international armed conflicts (IACs), ruses are likewise licensed in non-international armed conflicts under customary international law. But modern applications of misinformation or more accurately, disinformation call into question its reflexive characterization in IHL as a ruse for several reasons. First, while ruses are presented in source materials as being intended to mislead an “enemy” or “adversary”, disinformation campaigns during armed conflict today are instead often oriented primarily towards the civilian population. Under that obligation of IHL, Militaries can mislead their enemies on the battle field, but they cannot misguide or mislead the population in International armed conflicts.

 Kashmir will be the part of extensive agenda, ahead of the 48th session; Pakistan has drafted a resolution seeking adoption with the goal of directing its anti-India rhetoric at Kashmir. Hurriyat Conference members are also invited at the conference that will highlight the humanitarian challenges and will remind the world to look upon the stance of Kashmiris. The last OIC’s summit which held in Pakistan, ended with the establishment of the OIC-led Humanitarian Trust Fund for Afghanistan to channel aid, as well as the designation of the OIC Secretary General’s Special Envoy to work alongside the UN in the war-torn country. Moreover, the members will review the previous decisions on Afghanistan in this session.
Kashmir will be the part of extensive agenda, ahead of the 48th session; Pakistan has drafted a resolution seeking adoption with the goal of directing its anti-India rhetoric at Kashmir. Hurriyat Conference members are also invited at the conference that will highlight the humanitarian challenges and will remind the world to look upon the stance of Kashmiris. The last OIC’s summit which held in Pakistan, ended with the establishment of the OIC-led Humanitarian Trust Fund for Afghanistan to channel aid, as well as the designation of the OIC Secretary General’s Special Envoy to work alongside the UN in the war-torn country. Moreover, the members will review the previous decisions on Afghanistan in this session.
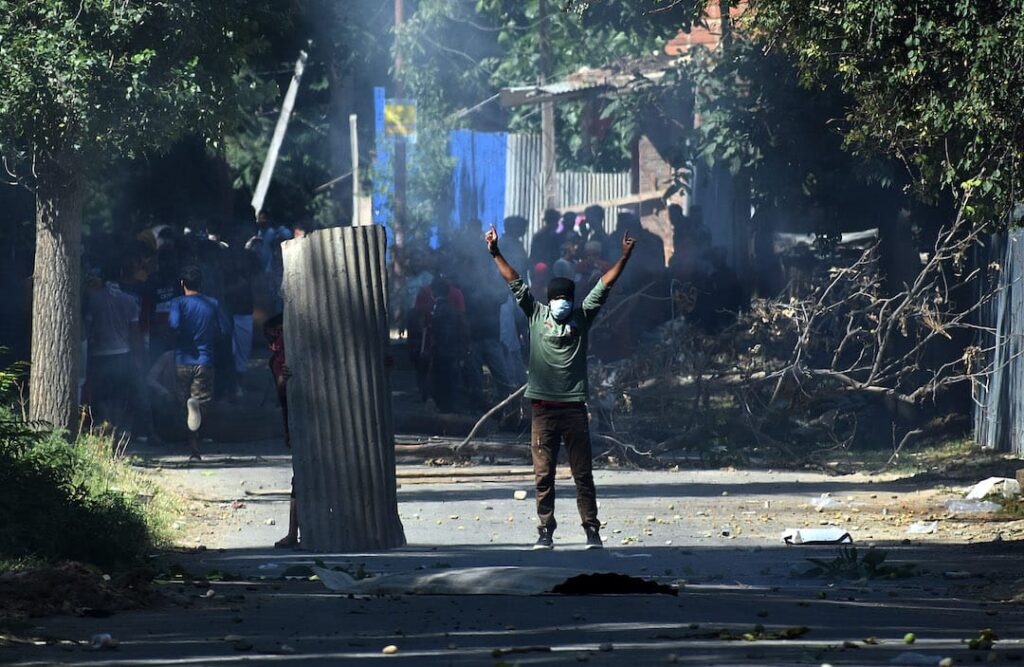

 In the context of conflicted areas, social activists, international organizations, independent news agencies use social media as a weapon to report human rights violation. State organized violence and mass killing highlights the stories of oppressed ones. In the region of Kashmir which is disputed territory between India and Pakistan. The social media have played an effective role during recent mass mobilization for “right to self-determination”. Indian administration imposed some serious censorship over digital and main stream media to cover up the human rights violations in the valley. Social media activism is posing a major challenge to the Indian state in Kashmir; most people are tending towards use of soft-power to empower their cause of right to self-determination.
In the context of conflicted areas, social activists, international organizations, independent news agencies use social media as a weapon to report human rights violation. State organized violence and mass killing highlights the stories of oppressed ones. In the region of Kashmir which is disputed territory between India and Pakistan. The social media have played an effective role during recent mass mobilization for “right to self-determination”. Indian administration imposed some serious censorship over digital and main stream media to cover up the human rights violations in the valley. Social media activism is posing a major challenge to the Indian state in Kashmir; most people are tending towards use of soft-power to empower their cause of right to self-determination.
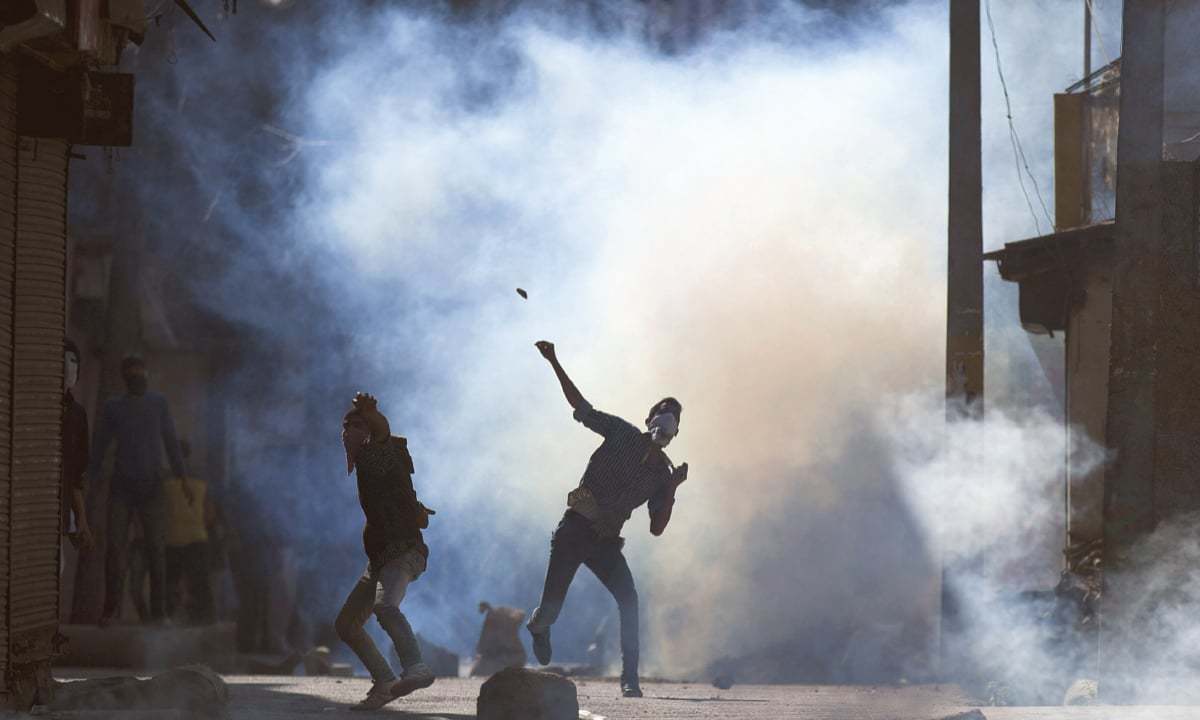 Kashmiri activists and artists came with new ideas to cope up with this situation and initiated campaigns using the instrument of Music, Culture and Poetry to support Kashmiris against the oppression of India. On September 20th 2019, Kashmiri artists, highlighted the theme of “Resist to Exist” with the collaboration from British-Kashmiri artist Sumaya Teli and Kashmiri-American artist, Nouf Bazaz. Through the collaboration of artists, the event shared stories of the Kashmiri struggle against Indian occupation and militarization and for the right to Kashmiri self-determination. It went viral in different parts of the world, and help youth to understand the Kashmir situation and Indian mistreatment of Kashmiri people. In the recent six to seven years, we have seen, how digital media revolutionized the Kashmir Conflict and created the environment where young researchers and activists can access the information to understand the conflict and to advocate the worth of freedom for the next generations.
Kashmiri activists and artists came with new ideas to cope up with this situation and initiated campaigns using the instrument of Music, Culture and Poetry to support Kashmiris against the oppression of India. On September 20th 2019, Kashmiri artists, highlighted the theme of “Resist to Exist” with the collaboration from British-Kashmiri artist Sumaya Teli and Kashmiri-American artist, Nouf Bazaz. Through the collaboration of artists, the event shared stories of the Kashmiri struggle against Indian occupation and militarization and for the right to Kashmiri self-determination. It went viral in different parts of the world, and help youth to understand the Kashmir situation and Indian mistreatment of Kashmiri people. In the recent six to seven years, we have seen, how digital media revolutionized the Kashmir Conflict and created the environment where young researchers and activists can access the information to understand the conflict and to advocate the worth of freedom for the next generations.
 Till 2014, “Two Track Diplomacy” was followed by the major powers as they encouraged Iran for diplomatic negotiations, at the same time sanctions were being imposed on Iran’s energy and finance sectors. All these events led to the nuclear deal, a landmark accord reached in 2015 which brought together the permanent members of UN Security Council and the European Union for a shared commitment. Under the deal, Iran dismantled much of its nuclear program and opened the nuclear sites for inspection, in return sanctions were lifted and Iran was allowed to make economic relations with the international community. Iran agreed to restrain nuclear activities and it was assured by US that no new sanctions will be imposed.
Till 2014, “Two Track Diplomacy” was followed by the major powers as they encouraged Iran for diplomatic negotiations, at the same time sanctions were being imposed on Iran’s energy and finance sectors. All these events led to the nuclear deal, a landmark accord reached in 2015 which brought together the permanent members of UN Security Council and the European Union for a shared commitment. Under the deal, Iran dismantled much of its nuclear program and opened the nuclear sites for inspection, in return sanctions were lifted and Iran was allowed to make economic relations with the international community. Iran agreed to restrain nuclear activities and it was assured by US that no new sanctions will be imposed.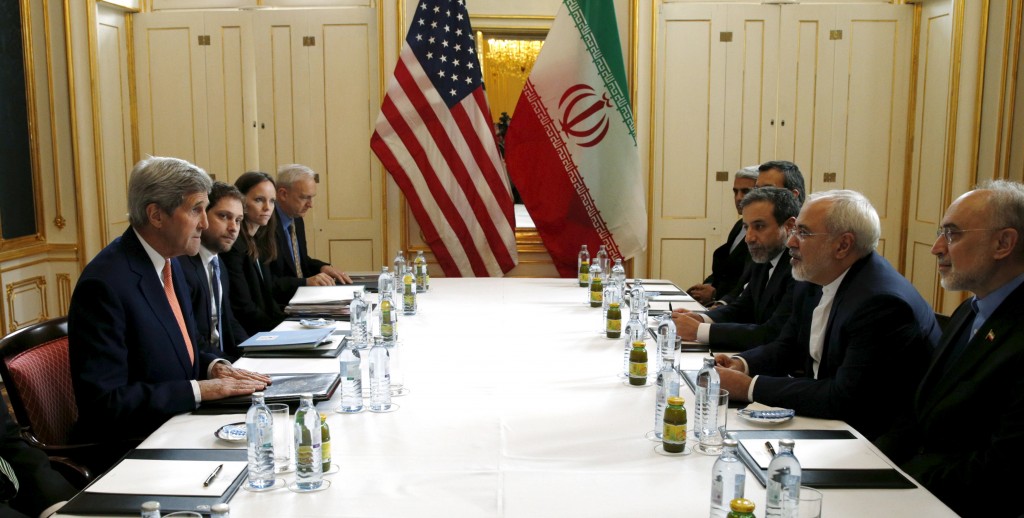 The Joe Biden administration after coming to power in 2021 pledged to revive the nuclear deal to which Iran also agreed on a condition of indirect involvement, talks resumed in November in Vienna. Last month on 23rd Feb 2022, a European Union representative to talks said “We are nearing the end” over the success or failure of renewed Iran nuclear deal. The next day Russia-Ukraine crisis erupted, for the UK, US and EU have imposed sanctions on Russia’s oil, gas and financial sector, trade and travel restrictions also made, in response to that Russia has also banned exports. According to the participants of talks, the deal was on the verge of being finalized after a year of discussions. But, last-minute demands from Russia, one of the deal’s signatories, have threatened to undermine the efforts to revive JCPOA. Russia has said it wants assurance that Western sanctions imposed on Moscow will not prohibit Russia from doing business and military cooperation with Iran. The outcome of the current intensive discussions in Vienna aimed at restoring Iran’s 2015 nuclear deal with world powers and Iran’s relationship with Russia now has to be foreseen in coming days.
The Joe Biden administration after coming to power in 2021 pledged to revive the nuclear deal to which Iran also agreed on a condition of indirect involvement, talks resumed in November in Vienna. Last month on 23rd Feb 2022, a European Union representative to talks said “We are nearing the end” over the success or failure of renewed Iran nuclear deal. The next day Russia-Ukraine crisis erupted, for the UK, US and EU have imposed sanctions on Russia’s oil, gas and financial sector, trade and travel restrictions also made, in response to that Russia has also banned exports. According to the participants of talks, the deal was on the verge of being finalized after a year of discussions. But, last-minute demands from Russia, one of the deal’s signatories, have threatened to undermine the efforts to revive JCPOA. Russia has said it wants assurance that Western sanctions imposed on Moscow will not prohibit Russia from doing business and military cooperation with Iran. The outcome of the current intensive discussions in Vienna aimed at restoring Iran’s 2015 nuclear deal with world powers and Iran’s relationship with Russia now has to be foreseen in coming days.
 Beijing’s policy towards Taipei is of deterrence, the goal is to stop Taiwan from formal independence, western support for Taiwan, and particularly US intervention. US policy towards Taipei is of “strategic ambiguity” in case of Beijing’s attack. Taiwan, a small island, yet it is of the utmost importance for China as well as the United States. On the basis of the geostrategic location of Taiwan in the Indo-Pacific region and to restrain the rise of China in global politics, strengthened military posture and influence in East Asia has shifted strategic objectives of US. The United States has been playing the “Taiwan Card” for the strategic rivalry with China. Apart from strategic, US have expanding economic as well as ideological objectives. Taiwan is the world’s largest chip manufacturer and the 10th biggest trading partner of Washington in the high-tech industry and semi-conductor production while supporting US economy with $600 Billion. Another strategic factor is that, when Taiwan will be under the jurisdiction of China, it would extend its missile ranges eastward by around 150 nautical miles. As a result, China would become the dominating force in the East China Sea, making it easier for Beijing to attack its rivals. US-China strategic competition and cross-strait relations are resulting in strong alignments among US and Taiwan.
Beijing’s policy towards Taipei is of deterrence, the goal is to stop Taiwan from formal independence, western support for Taiwan, and particularly US intervention. US policy towards Taipei is of “strategic ambiguity” in case of Beijing’s attack. Taiwan, a small island, yet it is of the utmost importance for China as well as the United States. On the basis of the geostrategic location of Taiwan in the Indo-Pacific region and to restrain the rise of China in global politics, strengthened military posture and influence in East Asia has shifted strategic objectives of US. The United States has been playing the “Taiwan Card” for the strategic rivalry with China. Apart from strategic, US have expanding economic as well as ideological objectives. Taiwan is the world’s largest chip manufacturer and the 10th biggest trading partner of Washington in the high-tech industry and semi-conductor production while supporting US economy with $600 Billion. Another strategic factor is that, when Taiwan will be under the jurisdiction of China, it would extend its missile ranges eastward by around 150 nautical miles. As a result, China would become the dominating force in the East China Sea, making it easier for Beijing to attack its rivals. US-China strategic competition and cross-strait relations are resulting in strong alignments among US and Taiwan. All the actors involved in the conflict have different perspectives over Taiwan depending upon their interests. When we look at the NATO’s objectives in China and Taiwan conflict, the European member countries of NATO have economic objectives that could be disrupted because of a military confrontation. US along with these NATO members has underscored the importance of Taiwan in terms of peace and stability in a joint statement. In opinion of China, Washington has destabilized the region with provision of weapons to Taiwan. Therefore, demands are being made by Beijing to withdraw its deployed troops in Taiwan while US has asked the former to stop proactive military activities in Taipei. This has increased the magnitude of rivalry between two states. Also, the tensions between Taiwan and China has reached the highest levels in past few years especially after 2016, when Taiwanese President held the office and rejected the Chinese territorial claim of Taiwan. Both China and America have potential to ignite military and economic war over the issue of Taiwan. For unification of Taiwan and “Greater China”, Beijing has a political strategy which involves a military component and US analysts see invasion as the only military option which pose a great risk of military confrontation. The international order will be in jeopardy after Taiwan war. If the war begins at Taiwan Strait, it is more likely that Taiwan would be a battlefront for the world’s two countries with most powerful military forces and will become Sino-America war than China vs. Taiwan. The conflict will affect the overall region that may turn into a war zone. Impacts will also be seen on global supply chains, financial and transportation links.
All the actors involved in the conflict have different perspectives over Taiwan depending upon their interests. When we look at the NATO’s objectives in China and Taiwan conflict, the European member countries of NATO have economic objectives that could be disrupted because of a military confrontation. US along with these NATO members has underscored the importance of Taiwan in terms of peace and stability in a joint statement. In opinion of China, Washington has destabilized the region with provision of weapons to Taiwan. Therefore, demands are being made by Beijing to withdraw its deployed troops in Taiwan while US has asked the former to stop proactive military activities in Taipei. This has increased the magnitude of rivalry between two states. Also, the tensions between Taiwan and China has reached the highest levels in past few years especially after 2016, when Taiwanese President held the office and rejected the Chinese territorial claim of Taiwan. Both China and America have potential to ignite military and economic war over the issue of Taiwan. For unification of Taiwan and “Greater China”, Beijing has a political strategy which involves a military component and US analysts see invasion as the only military option which pose a great risk of military confrontation. The international order will be in jeopardy after Taiwan war. If the war begins at Taiwan Strait, it is more likely that Taiwan would be a battlefront for the world’s two countries with most powerful military forces and will become Sino-America war than China vs. Taiwan. The conflict will affect the overall region that may turn into a war zone. Impacts will also be seen on global supply chains, financial and transportation links. The current ongoing war launched between Russia and Ukraine can also have an influence on China over Taiwan. Earlier, US intelligence chief stated; ‘’China’s interpretation of western reaction is being observed by Washington’’. Some experts have suggested that Ukraine crisis might encourage China to take military action against Taiwan, if it becomes necessary. President of US, Joe Biden has sent an extraordinary delegation of officials in wake of Ukraine-Russia war to warn China and declared Washington’s strong support for Taiwan. Meanwhile, the Chinese ambassador to Washington has also alerted US of military confrontation risk over Taiwan. The increasing tensions between Sino-US relations and cross-strait relations can be a flashpoint of military confrontation.
The current ongoing war launched between Russia and Ukraine can also have an influence on China over Taiwan. Earlier, US intelligence chief stated; ‘’China’s interpretation of western reaction is being observed by Washington’’. Some experts have suggested that Ukraine crisis might encourage China to take military action against Taiwan, if it becomes necessary. President of US, Joe Biden has sent an extraordinary delegation of officials in wake of Ukraine-Russia war to warn China and declared Washington’s strong support for Taiwan. Meanwhile, the Chinese ambassador to Washington has also alerted US of military confrontation risk over Taiwan. The increasing tensions between Sino-US relations and cross-strait relations can be a flashpoint of military confrontation.
 Keeping good relations with Pakistan had been beneficial for U.S since it could contain the economic influence of China. Now, when China has involved Pakistan and many other South Asian regions in its economic activities like CPEC and BRI, still, no counter-strategy is visible from the U.S’s side. There is a big possibility that U.S foreign policy is focusing on the other regions (like the Middle East, Europe or Central Asia) and will shift again towards South Asia. This fact cannot be denied that countering China’s economic hegemony in the top priority of U.S’s Foreign policy and it might be secretly working to counter this. China is filling the vacuum left by U.S in different regions for example, RCEP which is Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership is the first multi-lateral free trade agreement that aims to create a consolidated market for the 10 member countries and their trade partners. RCEP in an agreement signed between 10 ASEAN states and also China, Japan, South Korea, New Zealand, Australia are signatory states. These countries contribute 29 percent to the world’s economy. This agreement has the potential to provide liberal facilities and a competitive investment environment in the Asia-Pacific region. China joined RCEP in response to the US-led Trans-Pacific Partnership. Also, COVID 19 led the countries to join this economic emancipation. This will extend the China’s influence in Asia-Pacific, and it is perceived that this is how it is countering US strategic pivot to Asia. RCEP is seen to be a political victory and not just an economic victory. U.S political influence in this region can also decrease. RCEP also gives an opportunity in wake of the decoupling of China. This may improve China’s perception and relation with Southeast Asian nations. America exports around 5.3 billion goods to Japan but it will now decrease since Japan will have better access to Chinese firms. RCEP impels U.S to respond to geopolitical primacy in the region. India did not participate in RCEP because according to them their local economy will be affected but on the other hand, it will also affect India’s look East policy. India can however collaborate with U.S more. CPEC and RCEP will have a linkage. It can also create economic opportunities for Afghanistan. Pakistan will have stronger relations with China. This will create two blocks “Indo- U.S” and “Pak- China” block. According to the US president Biden, America has to align with other democracies.
Keeping good relations with Pakistan had been beneficial for U.S since it could contain the economic influence of China. Now, when China has involved Pakistan and many other South Asian regions in its economic activities like CPEC and BRI, still, no counter-strategy is visible from the U.S’s side. There is a big possibility that U.S foreign policy is focusing on the other regions (like the Middle East, Europe or Central Asia) and will shift again towards South Asia. This fact cannot be denied that countering China’s economic hegemony in the top priority of U.S’s Foreign policy and it might be secretly working to counter this. China is filling the vacuum left by U.S in different regions for example, RCEP which is Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership is the first multi-lateral free trade agreement that aims to create a consolidated market for the 10 member countries and their trade partners. RCEP in an agreement signed between 10 ASEAN states and also China, Japan, South Korea, New Zealand, Australia are signatory states. These countries contribute 29 percent to the world’s economy. This agreement has the potential to provide liberal facilities and a competitive investment environment in the Asia-Pacific region. China joined RCEP in response to the US-led Trans-Pacific Partnership. Also, COVID 19 led the countries to join this economic emancipation. This will extend the China’s influence in Asia-Pacific, and it is perceived that this is how it is countering US strategic pivot to Asia. RCEP is seen to be a political victory and not just an economic victory. U.S political influence in this region can also decrease. RCEP also gives an opportunity in wake of the decoupling of China. This may improve China’s perception and relation with Southeast Asian nations. America exports around 5.3 billion goods to Japan but it will now decrease since Japan will have better access to Chinese firms. RCEP impels U.S to respond to geopolitical primacy in the region. India did not participate in RCEP because according to them their local economy will be affected but on the other hand, it will also affect India’s look East policy. India can however collaborate with U.S more. CPEC and RCEP will have a linkage. It can also create economic opportunities for Afghanistan. Pakistan will have stronger relations with China. This will create two blocks “Indo- U.S” and “Pak- China” block. According to the US president Biden, America has to align with other democracies.