Pakistan’s Justification and International Implications to the Deportation of Afghan Refugees
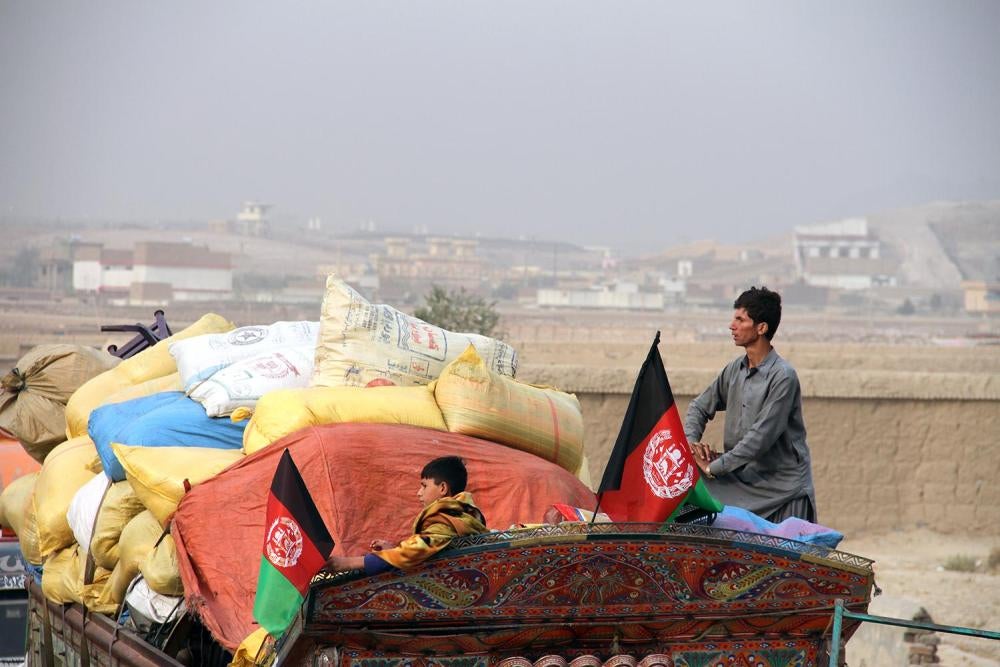

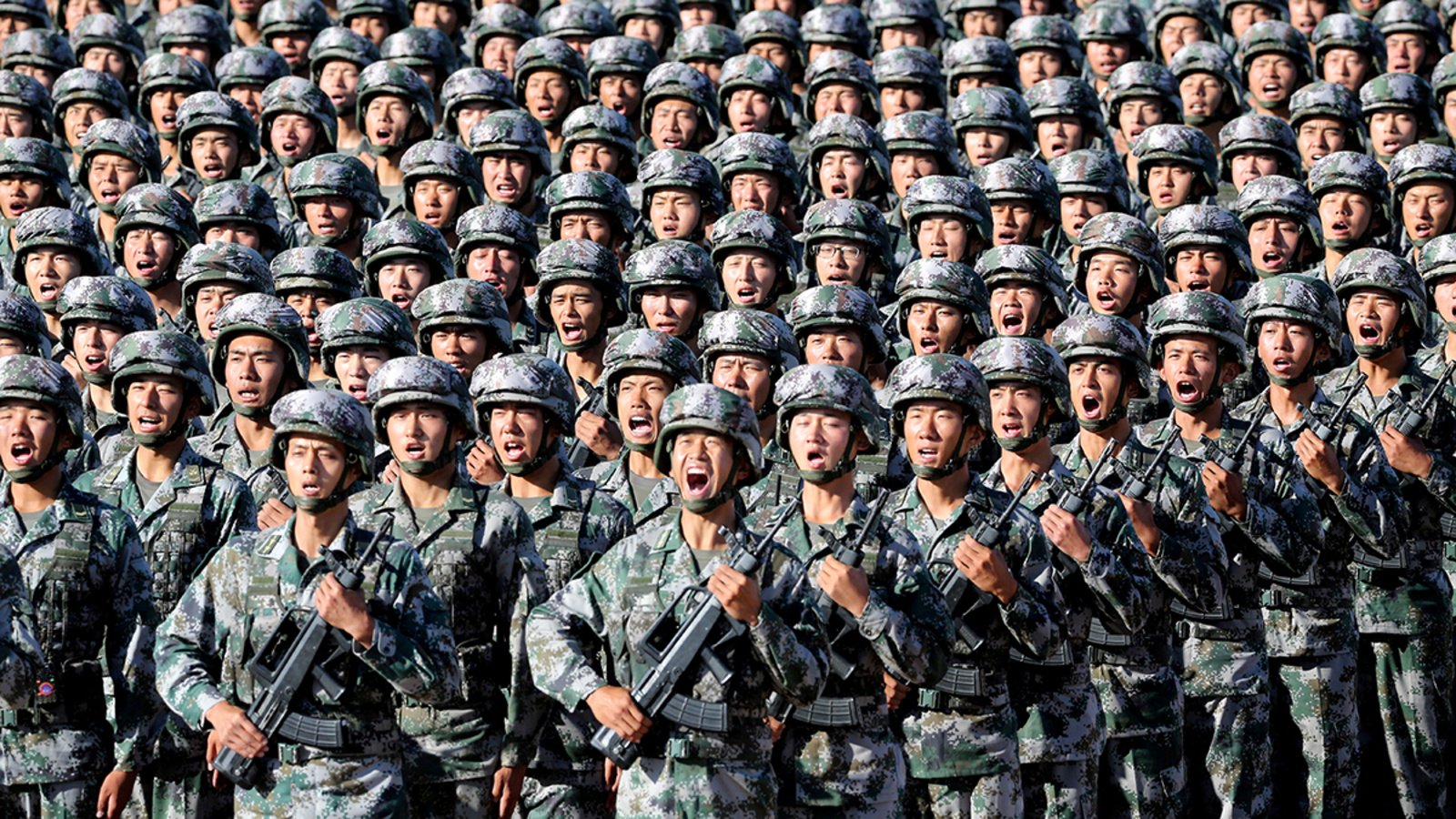
The people of Afghanistan have suffered greatly because of the US-Afghan war. Although many people would believe that the goal of war was to bring about stability in the area, there have been more negative effects than positive ones. Many Afghanis have migrated to Pakistan out of fear for the Taliban administrations ever after the United States formally declared the war to be finished. The Taliban are well-known for their extreme ideologies and stern adherence to Shariah law. The Taliban have now established their authority because of the withdrawal. Due to its proximity, most Afghan refugees are in Pakistan in quest of a better life. The international community has fully boycotted the Taliban administration during their control, which has left a financial gap. The current methods of running the Afghan economy include trafficking, smuggling, and the cultivation of opium.
The Afghani currency has decreased by 25% over the last two years, however it is evident that this has caused a significant increase in youth unemployment. According to reports, the joblessness rate reached 20% in 2023 and the disparity continued to worsen.
Afghani refugees have long considered Pakistan to be a safe shelter. To sustain their family, many refugees have already created businesses and residences registered under local Pakistani companies. However, these migrants are not given an identity. Afghans are experiencing an identity crisis as a result of being denied access to necessities like driver’s licenses and medical facilities, among other things. Although Pakistan does receive funding from other countries for the purpose of rehabilitating refugees, the living conditions in these camps are subpar and precarious. They lack proper access to medical care, lavatories, education, and leisure activities. A majority of the children in these camps for refugees are malnourished and at risk of contracting fatal illnesses.
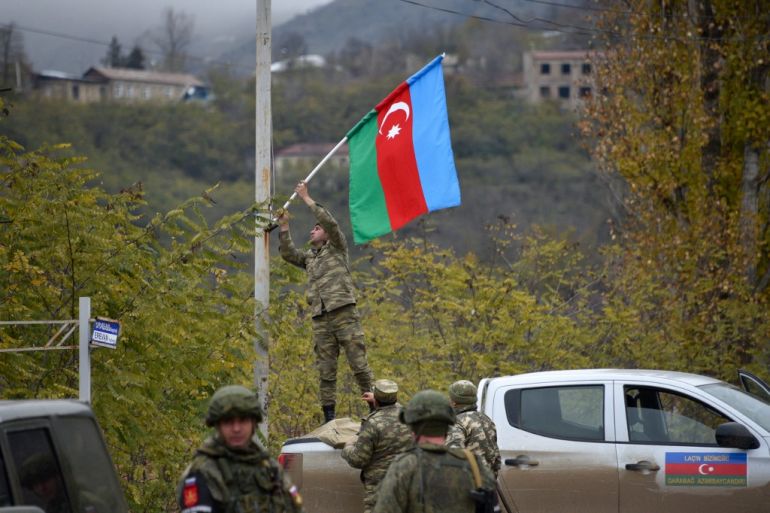
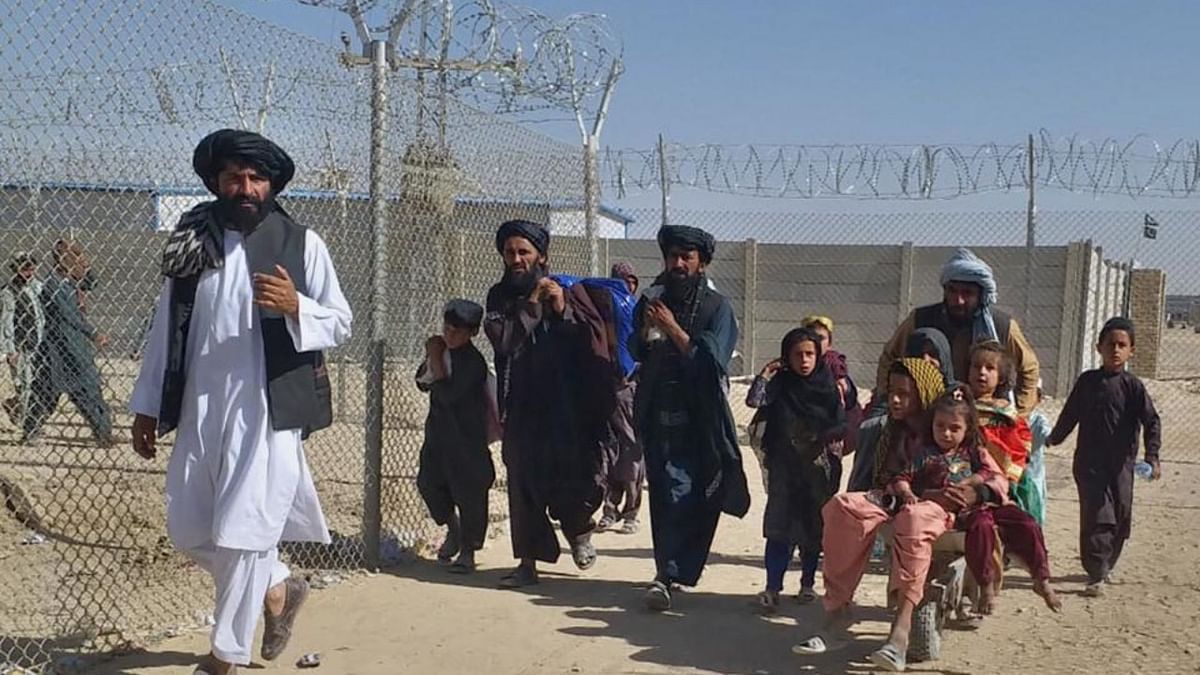 A legislation pertaining to the deportation of 1.7 million refugees who were not officially registered with the Pakistani government was recently passed. Considering this, legislation is currently being implemented, and a nationwide crackdown has been launched after the time for voluntary returns collapsed. The most recent influx of refugees was of 600,000 consequently after the Taliban takeover in Afghanistan. The question that arises is that, is it a viable solution for countries to forcibly deport refugees into countries where they have previously faced persecution?
A legislation pertaining to the deportation of 1.7 million refugees who were not officially registered with the Pakistani government was recently passed. Considering this, legislation is currently being implemented, and a nationwide crackdown has been launched after the time for voluntary returns collapsed. The most recent influx of refugees was of 600,000 consequently after the Taliban takeover in Afghanistan. The question that arises is that, is it a viable solution for countries to forcibly deport refugees into countries where they have previously faced persecution?
It’s a question of security for the host country but how does that reflect upon the international community. According to the refugee and human rights legislation, the principle of non-refoulement is recognized by international law. The principle of non-refoulement forbids sending a refugee back to a place where they risk persecution, torture, or cruel or inhumane treatment. This means that Pakistan must uphold the principle of non-refoulement and refrain from sending refugees against their will back to a nation where they risk persecution.
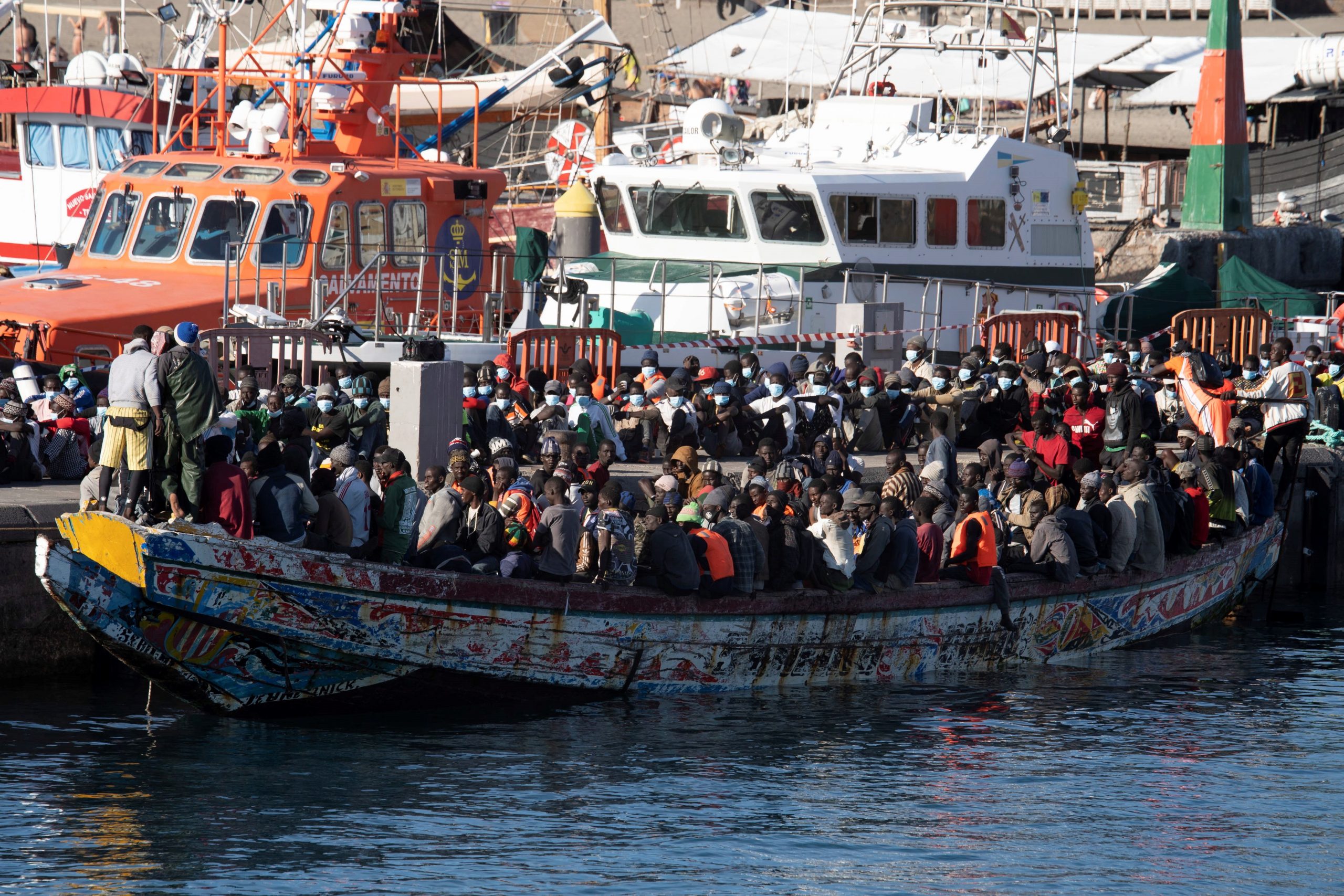
The Pakistani government found it rational to house refugees in transportation containers and leave them stranded at the Border of Afghanistan. This inhumane treatment led to a severe accident where the driver of the container collided on a bridge resulting in 2 deaths and 14 refugees severely injured. Some Afghan refugees in their primary schools said goodbye to their peers not knowing what waits for them beyond the border. While many refugees are being deported back, the Taliban government has requested Pakistan to be tolerant towards their people and to let them have their time to move back efficiently. Pakistan has rejected the call and claimed that,
“This action is a testament to Pakistan’s determination to repatriate any individuals residing in the country without proper documentation,” Pakistani Interior Minister Sarfaraz Bugti said on social media platform X.
Islamabad uses concerns about Afghans who have carried out suicide bombings in Pakistan to justify its policy towards undocumented foreign nationals. This is especially relevant given the recent spike in fatal attacks carried out by Taliban-affiliated militants operating out of Afghanistan. Protests to remove the country’s refugee population and anti-Afghan sentiments have been sparked by these violent episodes. Pakistan is currently experiencing a protracted economic crisis that has led to record-high rates of inflation and skyrocketing energy prices.

Amidst the deportations, there has been an increase in tension in the Parachinar region that borders Afghanistan. Sectarian violence is allegedly being created by rebel groups with deep ties to the Afghan Taliban Regime, although this is being done to push the Pakistani security forces to refocus their efforts within. The two main Muslim sects in Pakistan are now divided because of the 14 deaths caused by sectarian violence. Although some may view this as a diversion, if the Pakistani government does not address the issue effectively, it might cause even more chaos.
Pakistan must keep in mind that they are treading carefully in the event of guerilla warfare, even though security is still the government’s priority in the areas of the country that border Afghanistan. Since the Afghan refugees have lived in Pakistan for more than 30 years, their sudden departure will undoubtedly have negative effects on the country.
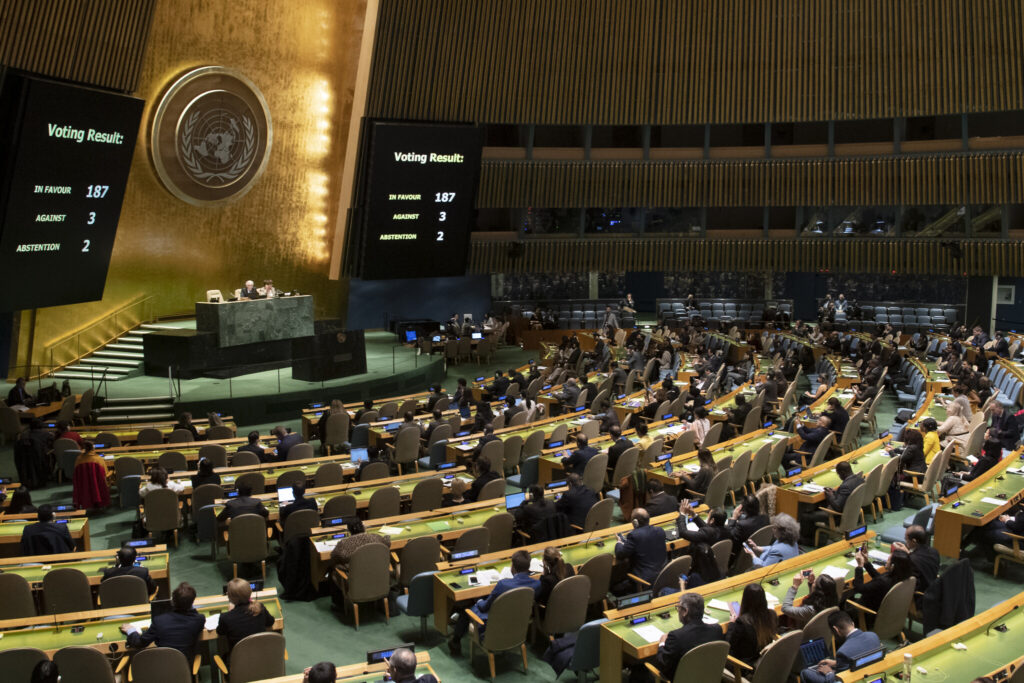


 Advancing the Cause of Regional Stability
Advancing the Cause of Regional Stability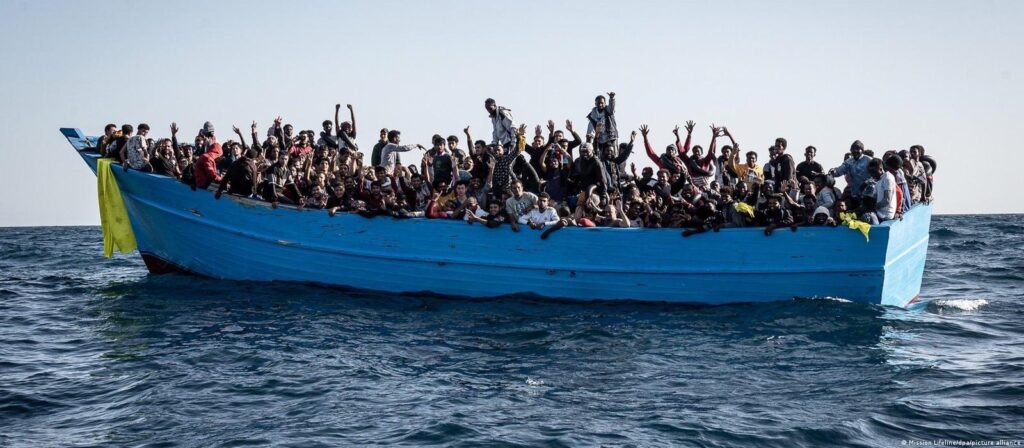
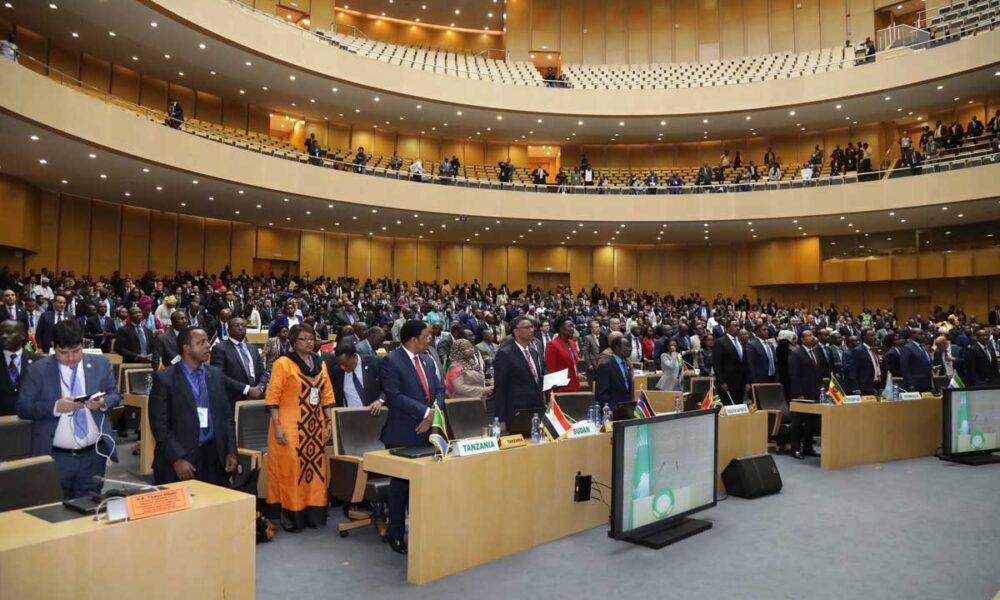



 The benefits that come along with this membership are that Africa will now be able to propose collaborative mechanisms with developed economies to counter the threat posed by climate change. This initiative will also encourage the developed world to tap the potential held by African continent. The African union will be heard as a collective voice when the global powers take important decision on climate, trade, and development. This membership would enforce good governance in the continent, as all the members of the G20 are committed to ensuring good governance and democracy. This would put pressure on the African states to uphold democracy and refrain from engaging in illicit methods of rule. In addition to this, the African union will also be able to initiate policies regarding investment with respect to climate change as Africa is a continent affected most by Climate change.
The benefits that come along with this membership are that Africa will now be able to propose collaborative mechanisms with developed economies to counter the threat posed by climate change. This initiative will also encourage the developed world to tap the potential held by African continent. The African union will be heard as a collective voice when the global powers take important decision on climate, trade, and development. This membership would enforce good governance in the continent, as all the members of the G20 are committed to ensuring good governance and democracy. This would put pressure on the African states to uphold democracy and refrain from engaging in illicit methods of rule. In addition to this, the African union will also be able to initiate policies regarding investment with respect to climate change as Africa is a continent affected most by Climate change. Nevertheless, the initiative taken by India is a commendable step to promote diversity and equal opportunity regardless of race or ethnicity. In my opinion, I believe this step was taken to compensate for the absence of Russia and China. This action may have been done for Russia to raise suspicion regarding its support to the African Sahel where the Western dominance is deteriorating. In the absence of China and Russia, the inclusion of the African Union in the G20 could help to balance the power dynamics within the group and make it more representative of the global community. Moreover, the Western Bloc could be a sending a message to Russia that African Union is aligned with western values and the West will meddle in the affairs of the African continent where Russia is involved economically and politically. On the contrary, It could also help to build stronger ties between Africa and the G20 countries. For example, the African Union is home to some of the world’s fastest-growing economies, such as Nigeria, Ethiopia, and Kenya. The inclusion of the African Union in the G20 would give these countries a greater say in global economic decision-making. It would also help to ensure that the G20 considers the needs of developing countries when developing its policies.
Nevertheless, the initiative taken by India is a commendable step to promote diversity and equal opportunity regardless of race or ethnicity. In my opinion, I believe this step was taken to compensate for the absence of Russia and China. This action may have been done for Russia to raise suspicion regarding its support to the African Sahel where the Western dominance is deteriorating. In the absence of China and Russia, the inclusion of the African Union in the G20 could help to balance the power dynamics within the group and make it more representative of the global community. Moreover, the Western Bloc could be a sending a message to Russia that African Union is aligned with western values and the West will meddle in the affairs of the African continent where Russia is involved economically and politically. On the contrary, It could also help to build stronger ties between Africa and the G20 countries. For example, the African Union is home to some of the world’s fastest-growing economies, such as Nigeria, Ethiopia, and Kenya. The inclusion of the African Union in the G20 would give these countries a greater say in global economic decision-making. It would also help to ensure that the G20 considers the needs of developing countries when developing its policies.
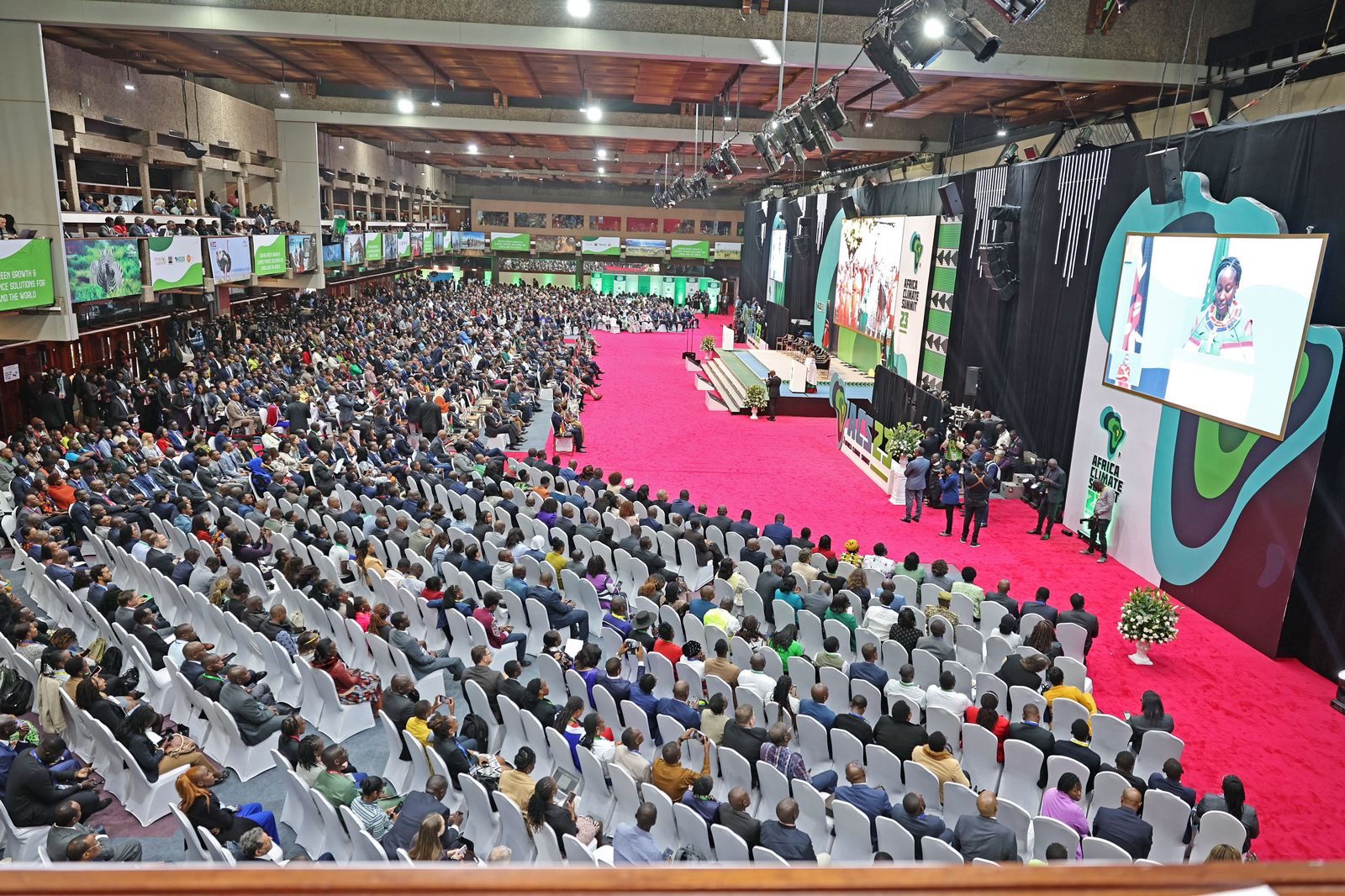






 Global leaders utilized the Climate Summit to announce funding commitments for sustainable development and green growth. A wide spectrum of stakeholders was present at the conference to debate and make pledges regarding climate action in Africa. Now is the moment to put words into action. Aside from increasing political will for climate action, the Africa Climate Summit 2023 has the ability to increase awareness of the continent’s climate action. There is a hope that the process of cutting greenhouse gas emissions will accelerate to tackle the effects of climate change, and creating a future for Africa and the world that is more climate resilient.
Global leaders utilized the Climate Summit to announce funding commitments for sustainable development and green growth. A wide spectrum of stakeholders was present at the conference to debate and make pledges regarding climate action in Africa. Now is the moment to put words into action. Aside from increasing political will for climate action, the Africa Climate Summit 2023 has the ability to increase awareness of the continent’s climate action. There is a hope that the process of cutting greenhouse gas emissions will accelerate to tackle the effects of climate change, and creating a future for Africa and the world that is more climate resilient.