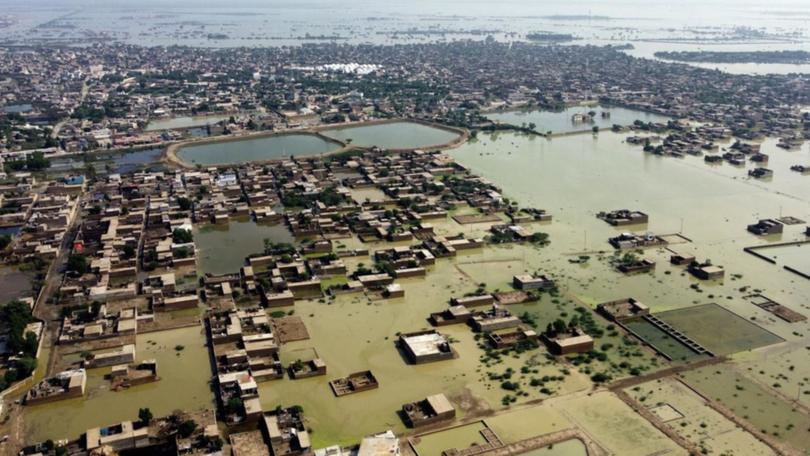
Global Flooding Crisis: Climate Change’s Widespread Devastation in Every Region
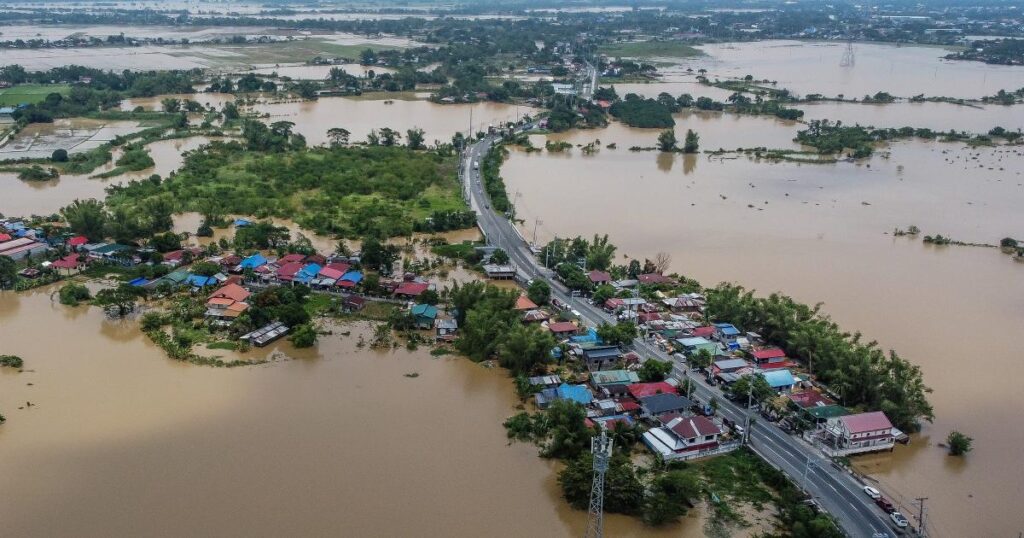

Introduction
Climate change is a global phenomenon that has given rise to a countless of environmental concerns, one of the most prominent being an increase in the frequency and intensity of floods. These catastrophic events, brought about by rising global temperatures and subsequent changes in rainfall patterns, are no longer confined to certain regions of the world. Instead, they now emerge as a major threat, consistently affecting multiple countries across the globe. From Asia to Africa, Europe to the Americas, floods have become a universal consequence of climate change, which is disrupting livelihoods, displacing communities, and devastating ecosystems. Consequently, understanding the causes, impacts, and potential solutions of climate change-induced floods becomes paramount as humanity faces the urgent need to mitigate and adapt to this pressing global crisis.
The Most Affected Countries across Regions due to 2023 Floods
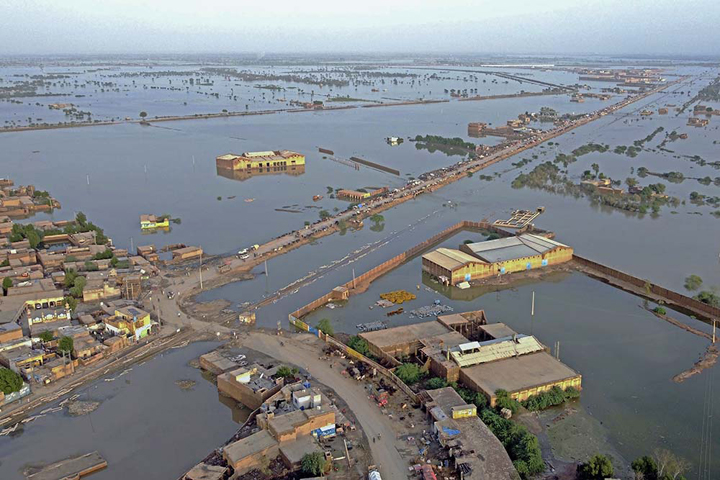
In Asia, the most affected countries by floods in 2023 were China, India, and Pakistan. In China, heavy rains caused flooding in southwestern China in July, killing at least 15 people and displacing thousands. In India, heavy rains caused flooding in the northeastern states of Assam and Meghalaya. As of July 21, 2023, the death toll from the 2023 floods in India has reached at least 108 people. The worst-hit state is Himachal Pradesh, where at least 88 people have died. Other states that have been affected by the floods include Uttar Pradesh, Punjab, Jammu and Kashmir, and Uttarakhand. The floods have also caused widespread damage to infrastructure and have destroyed thousands of houses. In Pakistan, heavy rains caused flooding in the northwestern provinces of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa and Punjab in July, killing at least 80 people and displacing thousands.
In addition, South Korea and Japan in East Asia, were hit hard due to floods, resulting in a tragic loss of life. At least 41 people lost their lives in South Korea and 12 in Japan due to these catastrophic events. Meanwhile, the Philippines in Southeast Asia was also severely impacted, with a death toll of at least 216. These floods left countless people displaced and in need of assistance.
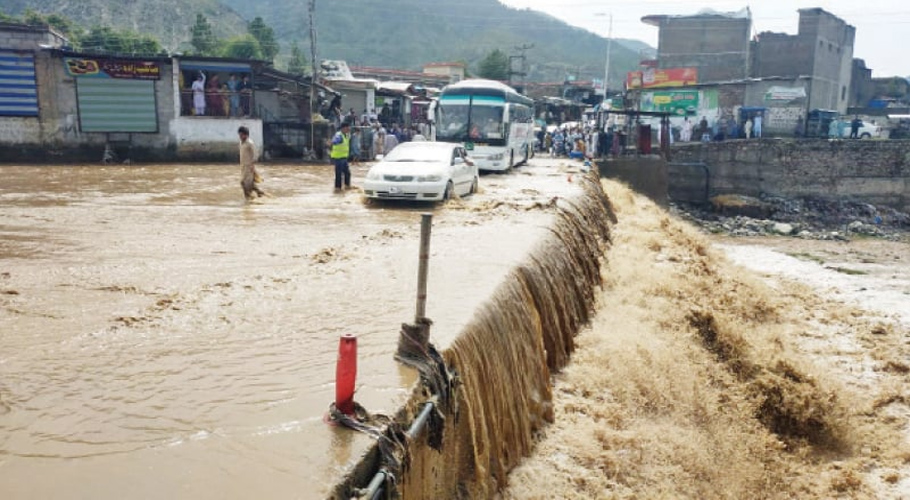 In Africa, the most affected countries by floods in 2023 were Rwanda, Ethiopia, and Mozambique. In Rwanda, torrential rains caused flooding in western and northern parts of the country, killing more than 130 people and resulted in displacement of huge number of people. In Ethiopia, heavy rains caused flooding in the Oromia and Somali regions due to which 240,000 people were impacted and, at least 120 people died. In Mozambique, heavy rains caused flooding in the Zambezi River basin in February, killing at least 70 people and displacing over 100,000 individuals.
In Africa, the most affected countries by floods in 2023 were Rwanda, Ethiopia, and Mozambique. In Rwanda, torrential rains caused flooding in western and northern parts of the country, killing more than 130 people and resulted in displacement of huge number of people. In Ethiopia, heavy rains caused flooding in the Oromia and Somali regions due to which 240,000 people were impacted and, at least 120 people died. In Mozambique, heavy rains caused flooding in the Zambezi River basin in February, killing at least 70 people and displacing over 100,000 individuals.
Europe: The most expensive natural hazard in Europe is flooding. Climate and socioeconomic developments are expected to make it worse in the future. In Europe, the most affected countries by floods in 2023 were Italy, Germany, and Belgium. In Italy, the deadly flooding that devastated much of northern Italy in late May, killing at least 15 people and displacing 40,000. In Germany, heavy rains caused flooding in the western state of North Rhine-Westphalia in July, killing at least 180 people and displacing over 100,000. In Belgium, heavy rains caused flooding in the eastern part of the country in July, killing at least 30 people and displacing over 10,000. The latest report by the European Commission lists the European cities and nations with the largest anticipated losses from future floods. Germany was reported to have the highest danger of flooding for residential structures, followed by France, Italy, and Spain.
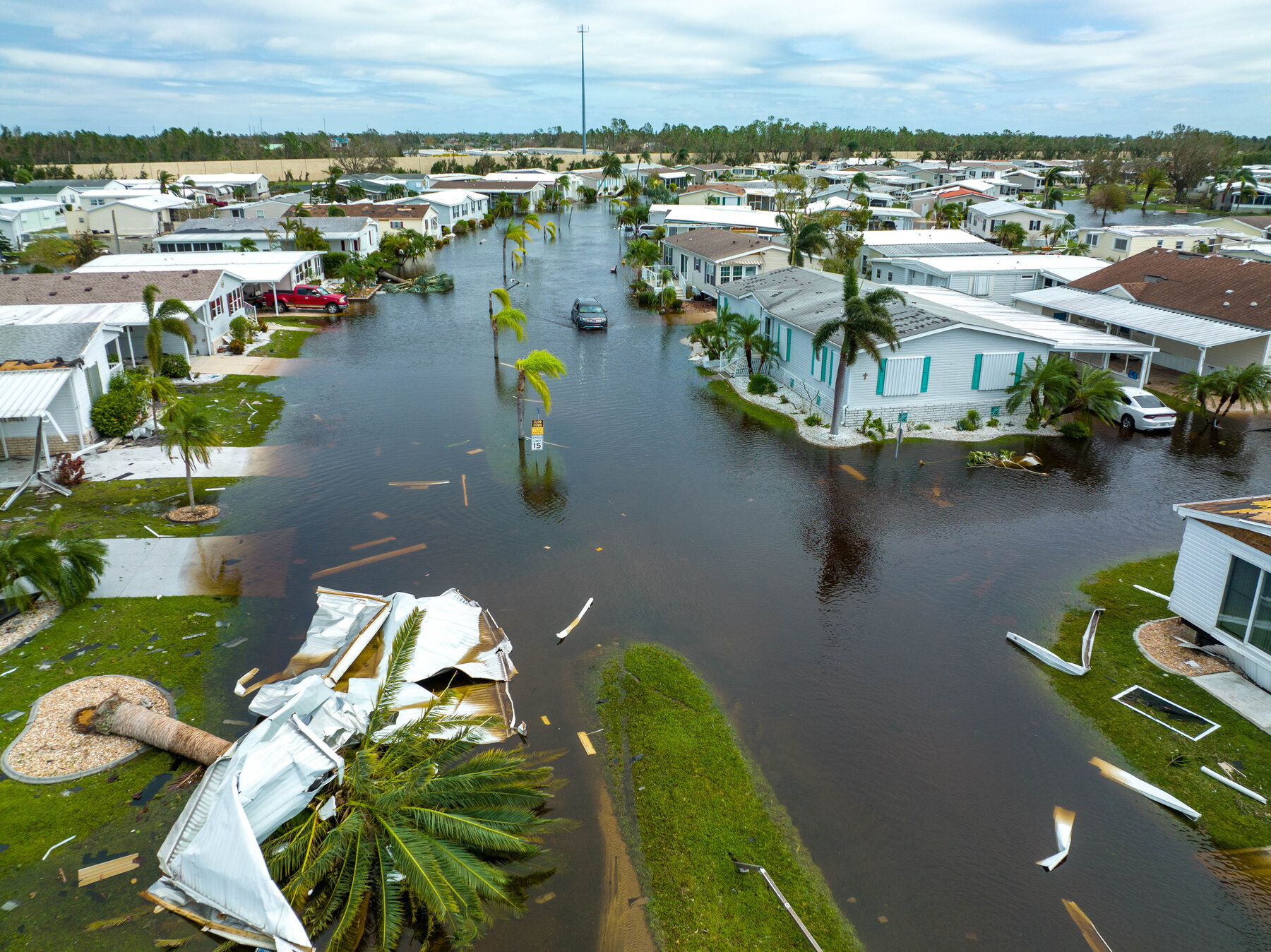
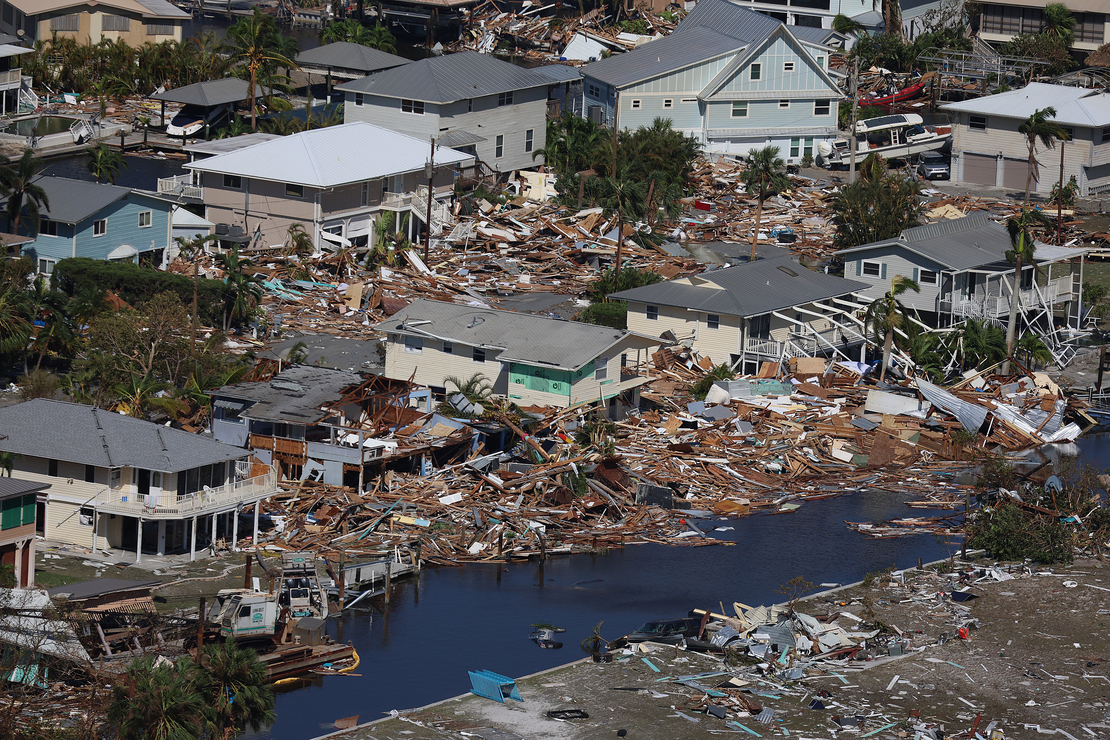
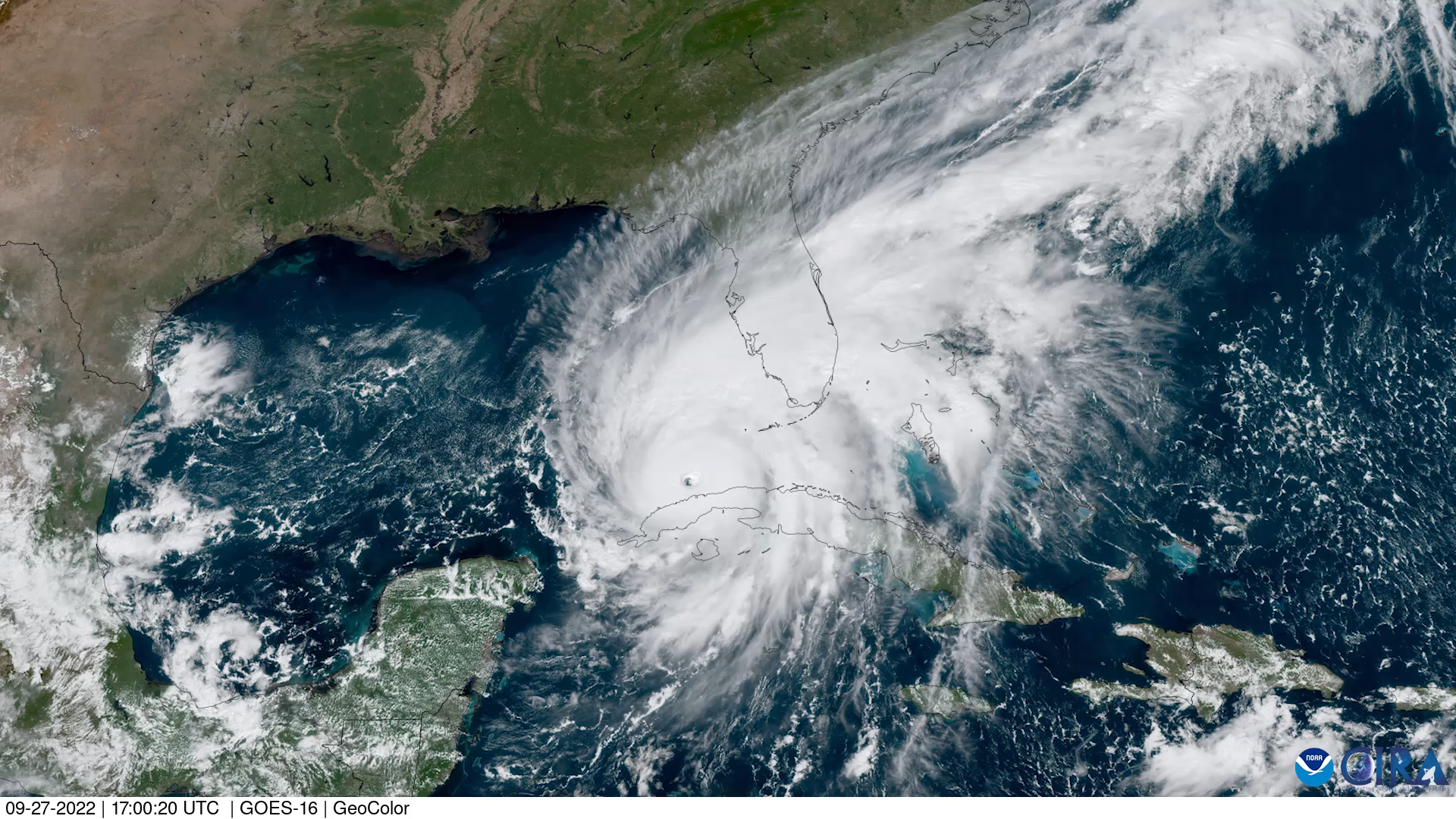
Americas: The floods have affected a number of countries in the Americas, including the United States, Canada, Mexico, Brazil, Colombia, Venezuela, and Ecuador. In North America, the most affected countries by floods in 2023 were the United States and Canada. In the United States, a series of storms caused flooding in the northeastern states of New York, New Jersey, and Pennsylvania in July, killing at least 11 people and causing widespread damage. There is also emergency in Kentucky due to flash flooding. In Canada, heavy rains caused flooding in the western Canada and caused forced evacuations.
To conclude, the global flooding crisis caused by climate change is devastating every region. Increased rainfall, rising sea levels, and melting glaciers have worsened the situation. This has resulted in loss of lives, infrastructure destruction, displacement, and damage to ecosystems. Mitigation and adaptation measures are needed to address this crisis, and it requires a collective effort. This includes reducing emissions to mitigate climate change and implementing resilient infrastructure to adapt to the increasing risks of global flooding. It is imperative that governments, communities, and individuals work together to tackle this widespread devastation and protect the planet Earth.


 Significance of Climate Justice and the Role of ICJ
Significance of Climate Justice and the Role of ICJ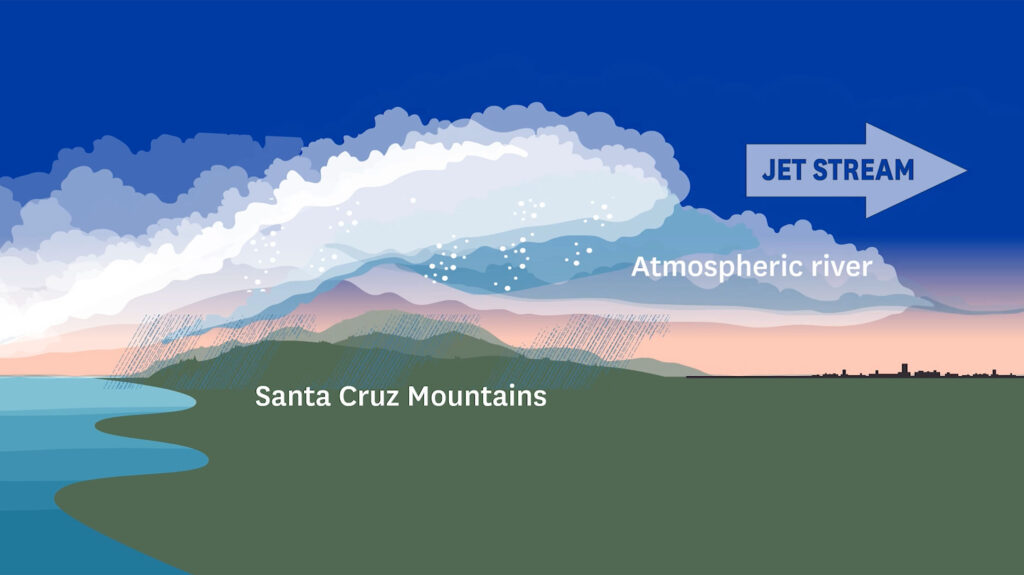
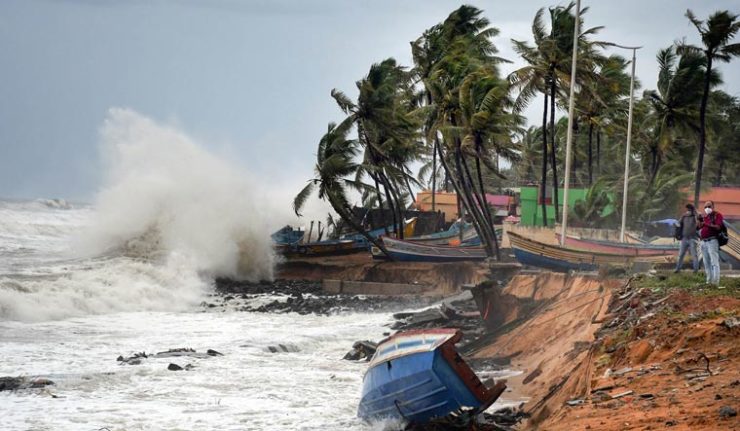
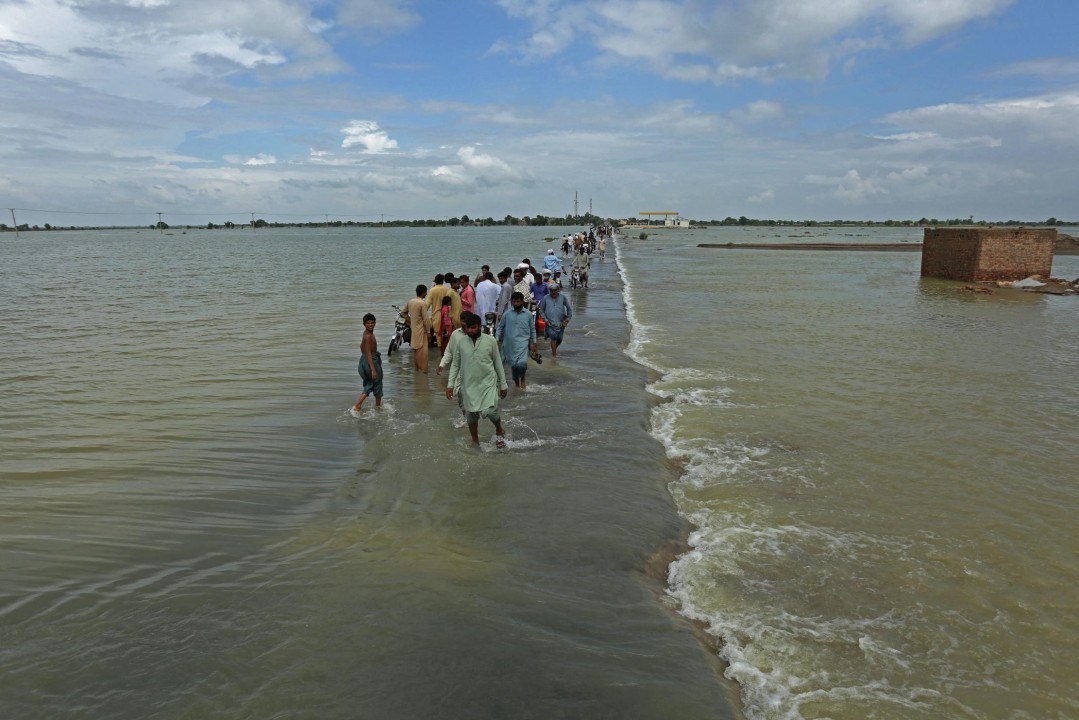
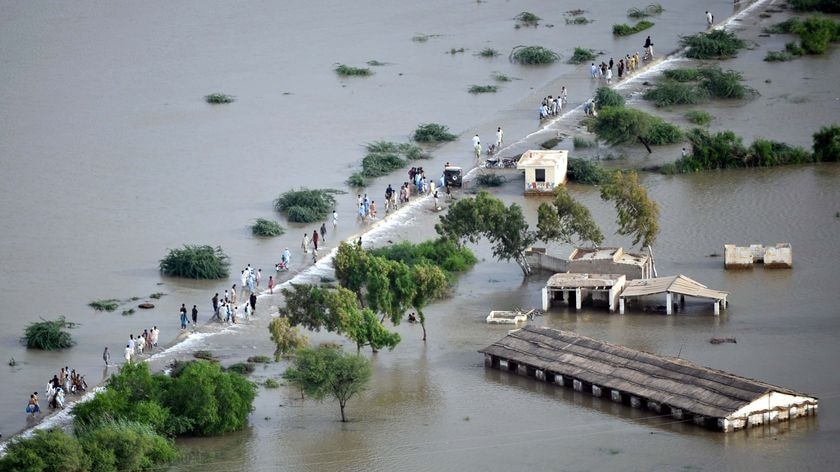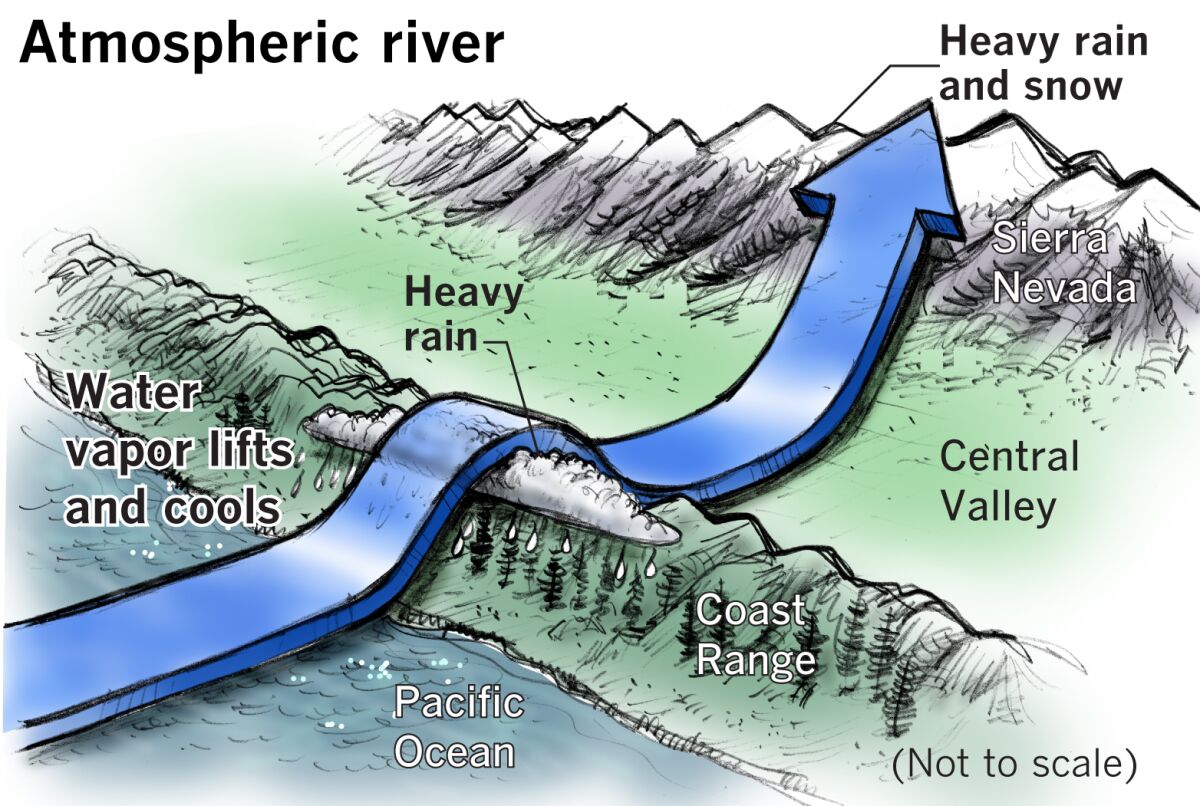










 Disasters can come in different forms. Industrial explosions or structural failures are examples of human-made disasters that are caused by errors made by humans. Earthquakes and floods are examples of physical events that result in natural disasters. Epidemics and armed conflicts are examples of complicated disasters. Whatever their shape, disasters cause community disruption and can have a significant negative impact on people, property, businesses, and the environment. They frequently exceed a community’s capacity for adjustment. The practice of efficiently anticipating and reacting to calamities is known as disaster management. In order to reduce the damage caused by disasters, resources should be strategically organized. The management of the duties associated with catastrophe prevention, readiness, response, and recovery also entails a systematic approach. It is now common knowledge that all hazards are natural and all disasters are the result of unfair anthropogenic interactions with nature. Although the latest flood has a different character compared to the one in 2010 the latter was a flash flood, while the current one is a river flood in both cases it can be argued that the damage caused by both disasters is a result of change.in demography and also ill-advised development policies throughout Pakistan. Some of the more immediate consequences of the latest disaster will be in the form of displacement, increase in illiteracy, unemployment, health crises, water and food shortages, infrastructure damage, loss of life, crop destruction, loss of livestock, water-borne diseases, urban migration and loss of social capital. Faced with these multifaceted challenges in such a short period of time, aid and humanitarian agencies must act and adapt quickly to alleviate the problems facing the millions of people who have been affected in recent weeks. Pakistan is vulnerable to most natural hazards. It is prone to floods, earthquakes, droughts and cyclonic storms. It is prone to famines and heavy monsoons. And let’s not forget the other kinds of disasters its residents inflict on each other the scourge of terrorism. With its second major flood in less than ten years, Pakistan is still having difficulty with the relief phase. It will be time to consider about disaster mitigation after this initial phase of assistance is finished.
Disasters can come in different forms. Industrial explosions or structural failures are examples of human-made disasters that are caused by errors made by humans. Earthquakes and floods are examples of physical events that result in natural disasters. Epidemics and armed conflicts are examples of complicated disasters. Whatever their shape, disasters cause community disruption and can have a significant negative impact on people, property, businesses, and the environment. They frequently exceed a community’s capacity for adjustment. The practice of efficiently anticipating and reacting to calamities is known as disaster management. In order to reduce the damage caused by disasters, resources should be strategically organized. The management of the duties associated with catastrophe prevention, readiness, response, and recovery also entails a systematic approach. It is now common knowledge that all hazards are natural and all disasters are the result of unfair anthropogenic interactions with nature. Although the latest flood has a different character compared to the one in 2010 the latter was a flash flood, while the current one is a river flood in both cases it can be argued that the damage caused by both disasters is a result of change.in demography and also ill-advised development policies throughout Pakistan. Some of the more immediate consequences of the latest disaster will be in the form of displacement, increase in illiteracy, unemployment, health crises, water and food shortages, infrastructure damage, loss of life, crop destruction, loss of livestock, water-borne diseases, urban migration and loss of social capital. Faced with these multifaceted challenges in such a short period of time, aid and humanitarian agencies must act and adapt quickly to alleviate the problems facing the millions of people who have been affected in recent weeks. Pakistan is vulnerable to most natural hazards. It is prone to floods, earthquakes, droughts and cyclonic storms. It is prone to famines and heavy monsoons. And let’s not forget the other kinds of disasters its residents inflict on each other the scourge of terrorism. With its second major flood in less than ten years, Pakistan is still having difficulty with the relief phase. It will be time to consider about disaster mitigation after this initial phase of assistance is finished.





