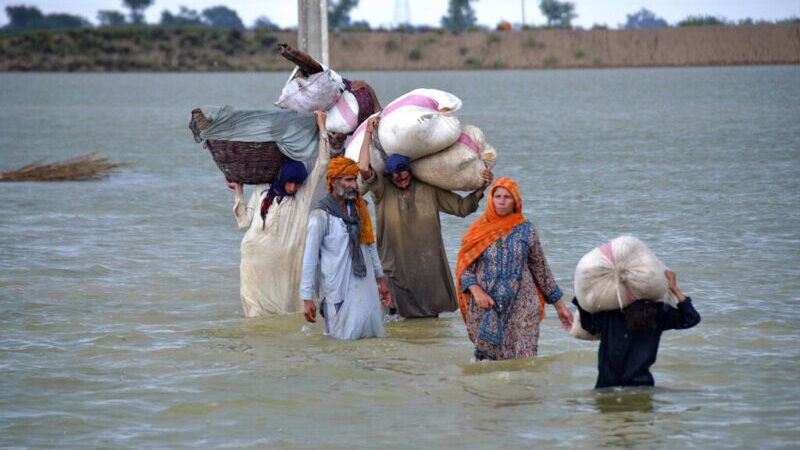
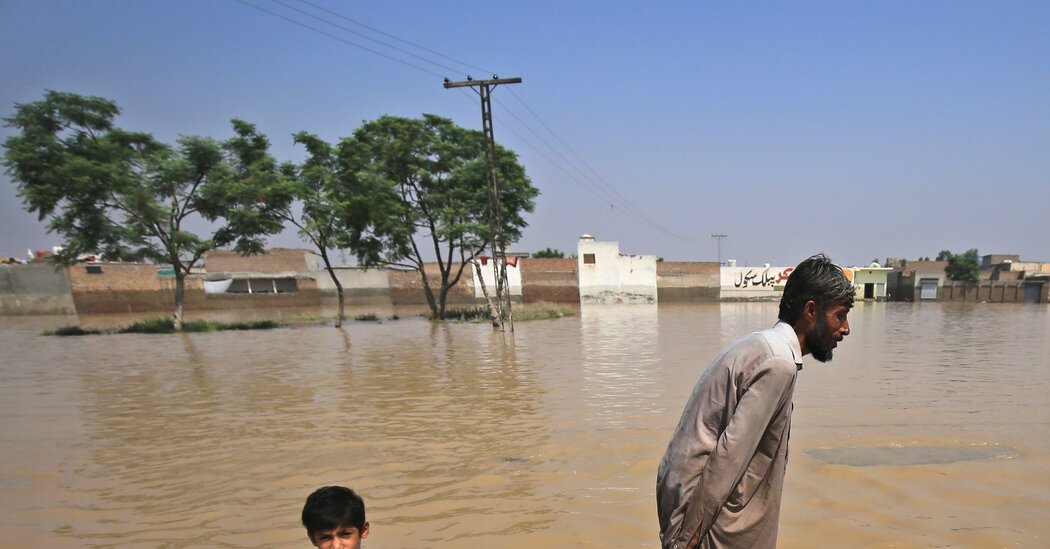
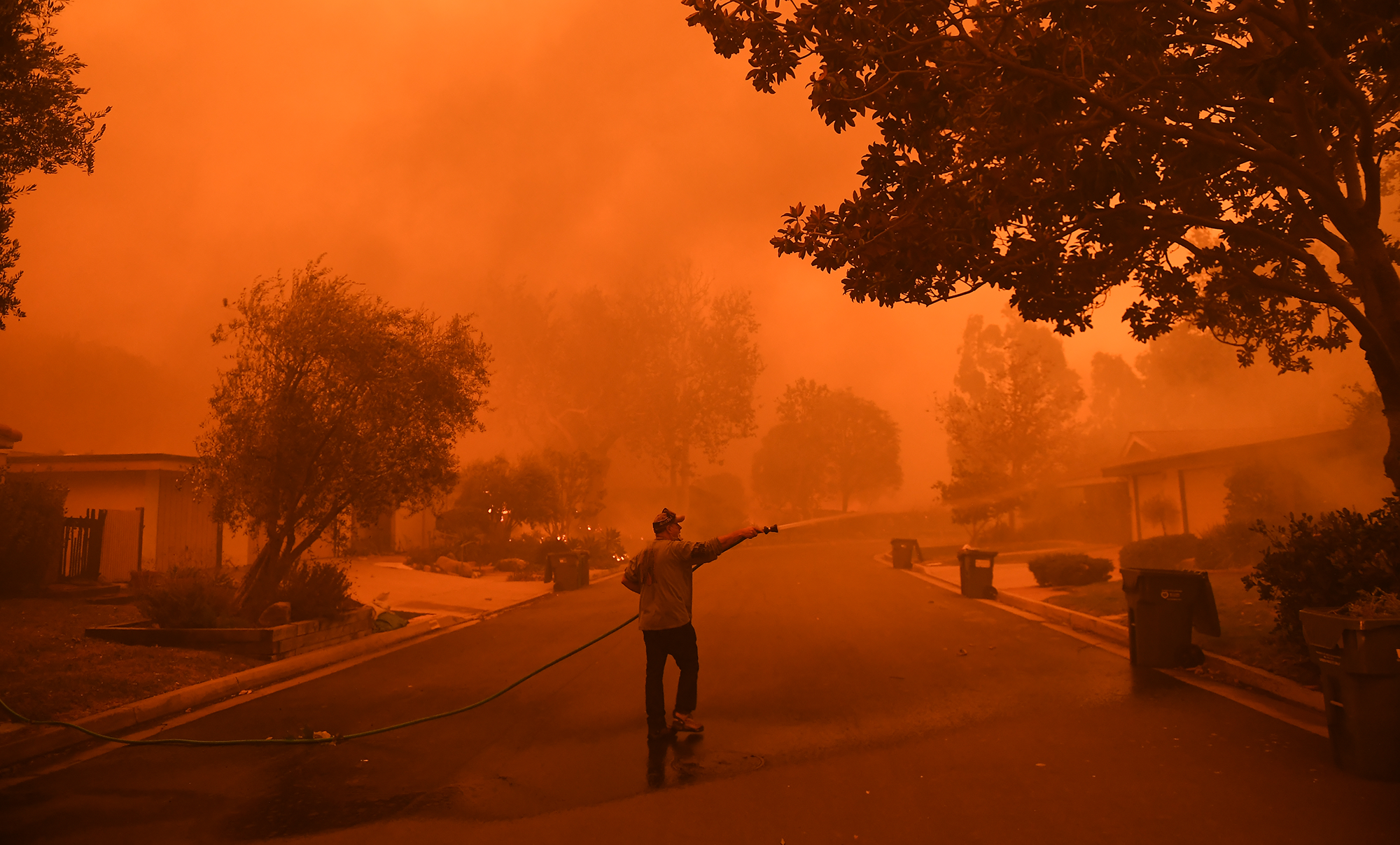
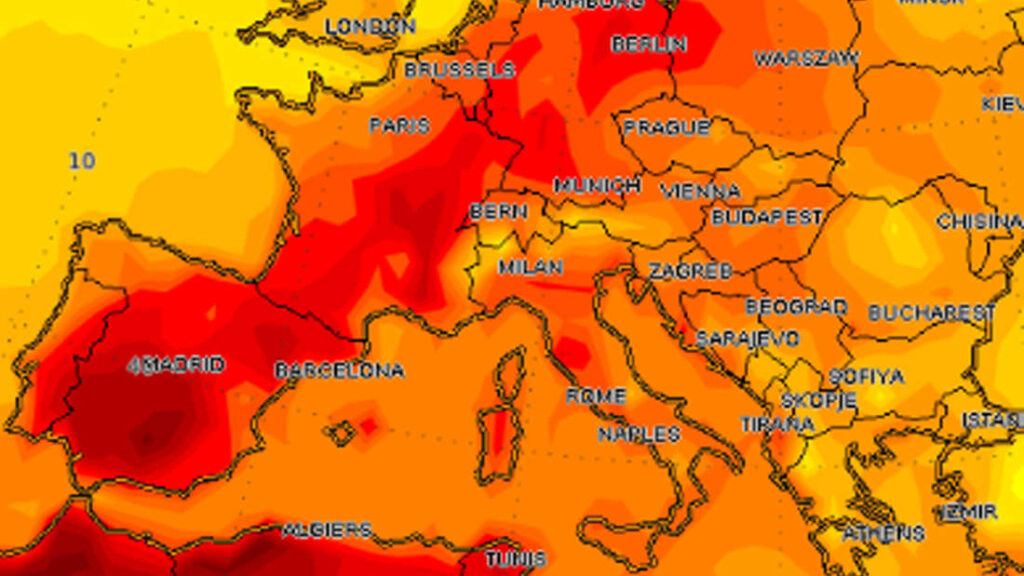
Climate change is not only an environmental challenge, rather it has evolved into a security and developmental challenge over the years for countries across the globe. In the annual report for 2020, Global Climate Risk Index has placed Pakistan in the fifth position on the list of countries that are most vulnerable to climate change. According to the report from 1999 to 2018, Pakistan has experienced 152 extreme weather hazards, faced economic loss worth $3.8 billion, and 9,989 people have died. Based on the statistics recorded by the think tank, the report concluded that Pakistan’s vulnerability to climate change is intensifying. The report points out that Pakistan is “recurrently affected by catastrophes [and] continuously rank among the most affected countries both in the long-term index and in the index for the respective year”. Due to the geographical location, Pakistan has become most vulnerable to climate change and hence placed on the long-term index of the report. One of the co-authors of the report David Eckstein registers in the report that “the entire region where Pakistan is located is prone to extreme weather events, in particular, heavy rainfalls e.g. during monsoon season and floodings as a result.
Regardless of the vulnerable status of Pakistan, the Biden administration did not invite leadership from Islamabad to participate in the climate change summit. Washington invited leaders from Russia, France, India, Indonesia, Germany, China, Italy, Bangladesh Kenya, Mexico, Denmark, Colombia, Congo, Chile, Jamaica, Argentina, Australia, Israel, Canada, Japan, Bhutan, and other countries to participate in the virtual climate change summit. Climate change activists and experts from Pakistan were surprised and annoyed on exclusion from the climate change conference, particularly when the country is not only the most affected one from the ever-intensifying repercussions posed by climate change but also when the key focus area of Pakistan Tehreek-e-Insaf government has been to combat this challenge. Prime Minister Imran Khan initiated the “Billion Tree Tsunami,†project as a step towards environmental protection.
According to Michael Kugelman, the U.S. based South Asian affairs expert explained the three conditions for being invited to the summit as “(1) close partner of the US or (2) a major polluter or (3) highly vulnerable to climate change or (4) some combo of 1,2,3. Pakistan certainly qualifies for (3). The second-largest emitter of carbon dioxide U.S. during the tenure of Donald Trump withdrew from the Paris Climate Agreement but Biden kept his election campaign promise and rejoined the agreement as soon as he entered the White House. Prime Minister Imran Khan in a tweet expressed that they “puzzled at the cacophony over Pak not being invited to a climate change conf! My govt’s environment policies are driven solely by our commitment to our future generations of a clean & green Pakistan to mitigate the impact of climate change.†However, countries from the same region as Pakistan such as Bangladesh, Russia, and India have been invited to the summit.

Pakistan’s leadership remains fully committed to addressing the concerns and threats of climate change. The initiatives taken to counter the grave consequences have been accepted and appreciated around the world by organizations such as WWF, World Economic Forum, and many other countries. The present government allocated Rs10 billion for facilitating the climate change programs that include sponsoring nature-based solutions, 10 billion tree projects, and cleaning of rivers. The exclusion of Pakistan from the virtual summit hardly makes sense and has been a source of constant debate as most other Asian countries have been invited. According to a survey held in 2019, 21 out of 30 most polluted cities in the world were in India. Air pollution is so grim in India that it has taken the lives of nearly 2 million people. An analysis published in Nature Climate Change Indias percentage of carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions rose slower in 2016-19 than in 2011-15 but was much above the world average of 0.7%. Union of Concerned Scientists published a report of 20 countries that emitted the most carbon dioxide in 2018, and India was placed third on the list. The irony is despite these reasons and Indias poor performance to meet the terms of the Paris Climate Agreement, the country was invited to the climate change summit.
Washington invited leaders of the Major Economic Forum on Energy and Climate that include 17 countries responsible for 80% of global emissions and GDP. The invitation was also given to the heads of countries that are extremely vulnerable to the aggravating status of climate change and simultaneously their governments are demonstrating strong initiatives to combat climate change. If analyzed from these criteria it can be concluded that Pakistan should have been invited to the summit but was deliberately ignored for different reasons. Kamran Yousaf, a senior Pakistani journalist stated that the elimination of Pakistan from attending the summit was not surprising considering the statements of the former US Ambassador to Pakistan, Cameron Munter, who remarked that “Pakistan has lost a great deal of importance in the minds of the leadership in Washington.†Many analysts perceived that this was a deliberate humiliation of Pakistan by the new administration in the U.S. and as a move to pressurize Pakistan to cooperate more with Washington in the Afghan Peace Process. This step taken by the leadership in the White House is also a manifestation of they view Pakistan and how it will frame future relations with the country, once the most important strategically. The surprising development has been deciphered by many other analysts also as a move to sideline Pakistan, especially during the time when new alliances in the region are forming that can challenge the superpower status of the United States.