There is a difference between patriotism and hyper nationalism: Muhammad Athar Javed in conversation with Salman Javed

Podcast | https://youtu.be/W4AOEM09Ksw
Scheduled for 9Pm tonight

Podcast | https://youtu.be/W4AOEM09Ksw
Scheduled for 9Pm tonight

Over the period of time, center of world economics and politics has been shifting from West to East. Resurgence of China and India as economic powers and their influence in Indian Ocean and South China Sea respectably opened window of opportunity for Asian struggling economies. The South China Sea in particular is a boiling pot of potential conflict and economic activities at the same time because of its strategic location and natural resources, with oil reserves of several billion barrels, an estimated nine hundred trillion cubic feet of natural gas. China’s claims over territories in South China Sea and its military buildup in Indian Ocean means that it will likely be a pivot point for global war and peace for the foreseeable future.
 Robert Kaplan a well-known journalist and political commentator, argued in his latest book “Asia’s Cauldron”, he turns to the South China Sea, a waterway that he describes as being “as central to Asia as the Mediterranean is to Europe”. If we look at the geographical significant of Asian Cauldron, it contains part of the Pacific Ocean, the South China Sea covers an area from Singapore and the Malacca Straits to Taiwan. It consists of more than 200 small islands, rocks and coral reefs, about three dozen of which are permanently above water. These are subject to overlapping claims from China, Vietnam, Malaysia and the Philippines. China as a big player in global economy lays claim to almost the entire South China Sea by feature of what is known as the “nine-dash line”. The sea is fast becoming “the most contested body of water in the world”, the main arena for geopolitical competition between a rising China and a US. With the rise of Dragon, the old order of American military unipolarity in the waters of the western Pacific is slowly fading. US strategic partnership with Japan, South Korea and India in Eastern hemisphere is the key to counter Chinese economic dominance. US motives to contain China is supplementary based on the security reasons rather than economic. China’s strategic aim must inevitably be to “exercise de facto hegemony over their own Asian Mediterranean”. Beijing wants to achieve its strategic goal while maintaining cordial relations with Western powers and tempering anxiety in Southeast Asia.
Robert Kaplan a well-known journalist and political commentator, argued in his latest book “Asia’s Cauldron”, he turns to the South China Sea, a waterway that he describes as being “as central to Asia as the Mediterranean is to Europe”. If we look at the geographical significant of Asian Cauldron, it contains part of the Pacific Ocean, the South China Sea covers an area from Singapore and the Malacca Straits to Taiwan. It consists of more than 200 small islands, rocks and coral reefs, about three dozen of which are permanently above water. These are subject to overlapping claims from China, Vietnam, Malaysia and the Philippines. China as a big player in global economy lays claim to almost the entire South China Sea by feature of what is known as the “nine-dash line”. The sea is fast becoming “the most contested body of water in the world”, the main arena for geopolitical competition between a rising China and a US. With the rise of Dragon, the old order of American military unipolarity in the waters of the western Pacific is slowly fading. US strategic partnership with Japan, South Korea and India in Eastern hemisphere is the key to counter Chinese economic dominance. US motives to contain China is supplementary based on the security reasons rather than economic. China’s strategic aim must inevitably be to “exercise de facto hegemony over their own Asian Mediterranean”. Beijing wants to achieve its strategic goal while maintaining cordial relations with Western powers and tempering anxiety in Southeast Asia.
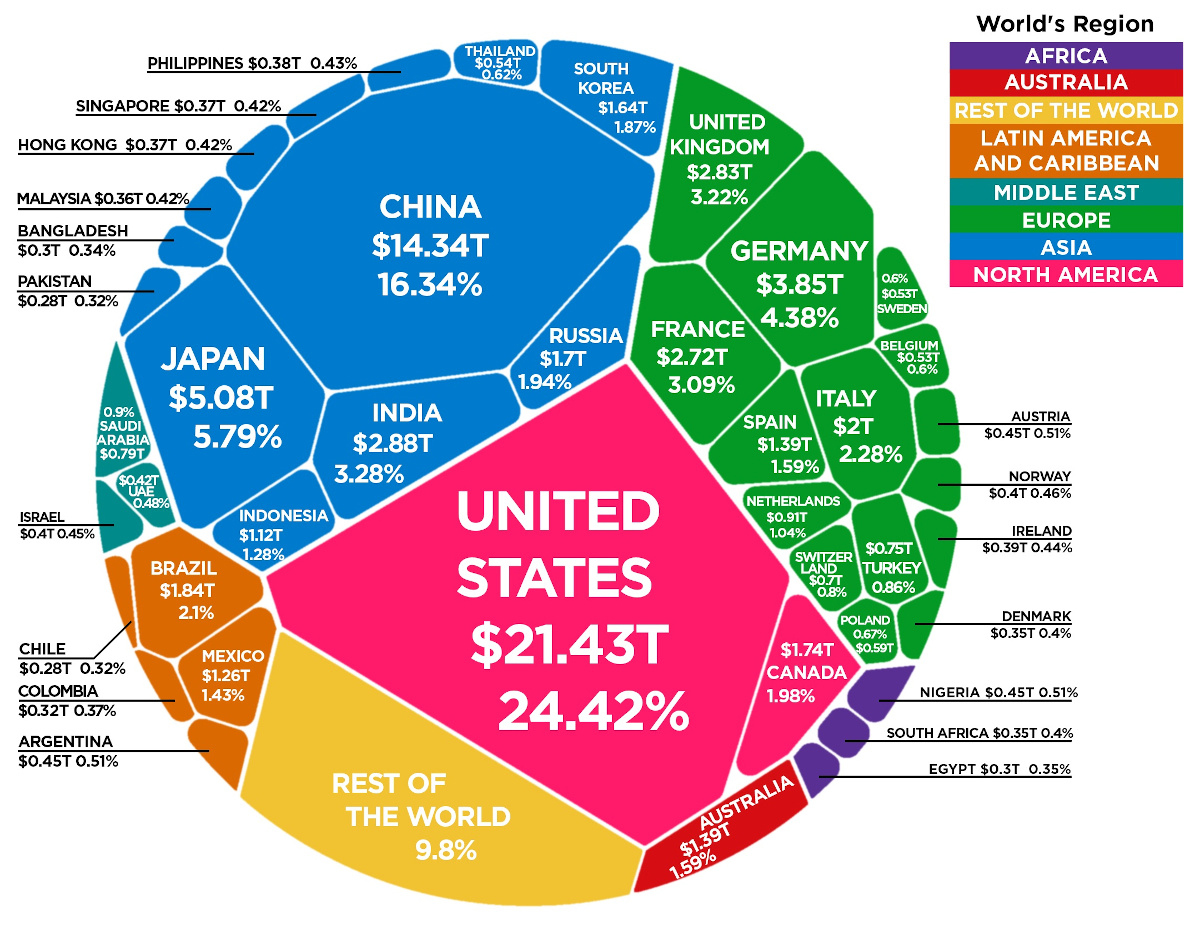
However, Modern China dominates world trade, following major reforms introduced in 1978 that were more focused on market-oriented economic development. The country’s economy is ranked at second position in the world after the United States, but China has been the world’s biggest exporter of goods since 2009 to up till now. China’s economy jumped 18.3% in 2021, compared to earlier years. In 2022, according to open data available on internet, China’s GDP worth is 14.236 trillion USD and it is rapidly increasing and sustains the 5.7% of economic growth bar. Moreover, China will overtake the US economy by 2028. The COVID-19 Pandemic and corresponding economic fallout have certainly tipped economic rivalry between China and West, and it ended in China’s favor. In Asian hemisphere, Japan is set to remain on 3rd position in World economic ranking with the GDP of 5.O6 trillion USD. In South Asia, India is also competing in economic race with 3.25 trillion USD worth of GDP. After overviewing the table, when Global economy is considered, Asian region is the most significant part of the world.
Apart from economic emergence, Cauldron States are perceiving the threat in South China Sea from China and its dream to be World super power. Therefore, they are pushing China, with an attempt to dominate the area even while acknowledging the presence and claims of other states in the South China Sea. China’s domination in the South China Sea would certainly clear the way for key Chinese air and naval influence throughout the Indian and Pacific Oceans. In that scenario, the US is at the center of the Asia-Pacific’s political and defense affairs which cannot be ignored. While most Southeast Asian states are cultivating their economic relations with China, they acknowledge the US’s role and in fact want the United States to remain involved in regional affairs. If only to be an effective balance to the rising economic and military power of China. The military superiority of the US is expected to offset China’s geographic, demographic and economic advantage.
 On the other hand, China expanding her influence by relying on relatively weak economic states to maintain its superiority in the region. China is practicing the Anti-Area Access Denial (2A-AD) strategy in South China Sea and beyond. Over the last two decades, Russian technologies combined with China’s efforts, including industrial espionage has gradually enhanced the capabilities of the People’s Liberation Army (PLA) to challenge U.S. forces in the Asia-Pacific region. The Anti-Aria Access Denial (A2/AD) is the strategy, with the aim of keeping out U.S. military intervention in its immediate areas of concern, including the disputed waters in the region.
On the other hand, China expanding her influence by relying on relatively weak economic states to maintain its superiority in the region. China is practicing the Anti-Area Access Denial (2A-AD) strategy in South China Sea and beyond. Over the last two decades, Russian technologies combined with China’s efforts, including industrial espionage has gradually enhanced the capabilities of the People’s Liberation Army (PLA) to challenge U.S. forces in the Asia-Pacific region. The Anti-Aria Access Denial (A2/AD) is the strategy, with the aim of keeping out U.S. military intervention in its immediate areas of concern, including the disputed waters in the region.
As above mentioned Pros and Cons, Asian Cauldron has its own significance in World economy and politics, alongside it would be boiling pot for potential conflict which might create uncertainty in international Affairs. US trade war with China, and US support to Taiwan as autonomic State are the circumstances of it. Thug of war between two world best economic powers might leave negative impact on the weaker states of the region in coming years.

Introduction:
The current repetition of interest in disinformation is not because the idea is innovative, but rather there is a growing consent that the digital revolution has greatly enhanced public vulnerability to manipulation by information, therefore, action needs to be taken to counter it. The related concept of propaganda has been around far longer, but many people see this as a means of driving engagement and mobilization for social or political change, rather than simply to mislead. The relatively new term ‘fake news’ covers a far wider range of content, often with financial motivations rather than political ones. Disinformation is the new tactical method in modern conflicts to create an environment where institutions can justify their violence, Governments can build their narratives and non-state actors preach their political ideology. Misinformation and fake news are new bombshells which are lunched from social platforms that leave impact on the human minds in large numbers. Modern militaries and actors in the conflict called this Hybrid warfare that is more effective and impactful than the actual military operations. Psychological operations by using the power of social media have become the part of military strategies in the realm of defense policies.
 Disinformation Impact on Human lives:
Disinformation Impact on Human lives:
According to the World Risk Poll, “fake news” topped the list of concerns for internet users in 2022. Military and civilian actors alike have made gainful use of disinformation in order to control the narrative regarding the conflict. The deep civil disintegration individuals of conflict settings amplifies the effect of such disinformation by creating echo chambers that intensify confirmation bias and accelerate the uncritical sharing of inaccurate events or reports. Practically, conflict-affected persons may be especially vulnerable to the ill effects of disinformation due to their frantic living conditions, elevated exposure to violence and lack of access to trustworthy sources of information. Compounding the potential for harm is the fact that conflict environments have proven especially fertile incubators for disinformation, as evident by its recent flourishing nature in Israel and Palestine, Libya, South Sudan, Syria, Ukraine and Yemen.
Russia-Ukraine Conflict:
In the recent confrontation between Russia and Ukraine, CNN reported that, “The Russian assault on Ukraine is not just an unprovoked attack on a sovereign nation that is producing horrific destruction and civilian torment. It is also the biggest war of the modern misinformation era”, some scholars argued that, Russia’s misinformation offensive impedes diplomatic efforts to end the war. Russian state media has portrayed Russian’s as victims of the war and covered the invasion as an attempt to liberate the Ukrainian population even as bombs and missiles rain down on civilians. On diplomatic forum, Russians has been denying the existence of war. Russian Foreign Minister Sergey Lavrov claimed with a straight face after talks with his Ukrainian counterpart in Turkey which, not surprisingly failed, that “Russia did not attack Ukraine”. It is an approach that has multiple payoffs for Moscow. It can be used as cover for atrocities and potential war crimes like the attack on the maternity hospital. Misinformation also plays into the Kremlin’s narrative about the nature of the war, that it is the victim, which is served up to Russians on state media networks. The Russian claims might be absurd but they also find an audience among conspiracy theorists on social media and can be used by propagandists, even in Western countries to cast doubt on the credibility of leaders building a united front against Moscow.
The disinformation fight:
The Oversight Board was created in 2020 by Zuckerberg but it is an independent body made up of former world leaders, activists and top lawyers to make decisions on the most significant content moderation challenges on Facebook and Instagram. Disinformation and misinformation are major challenges on these platforms and have always been important issues for the board because of the wide use of these social applications. Although social media companies have a big impact on people’s lives but the disinformation fight cannot be solved by Big Tech alone. United States and UN should step out to mitigate these challenges on domestic level as well as on international platforms. In Pakistan, Government had passed Prevention of Electronic Crimes Act (PECA), through ordinance to handle fake news and disinformation on social media. International Humanitarian Law (IHL) takes a remarkably lenient approach to such misinformation actions and stratagems with one exception. Combatants may not resort to perfidy, defined in Article 37 of Additional Protocol to the Geneva Conventions as “inviting the confidence of an adversary to lead him to believe that he is entitled to, or is obliged to accord, protection under the rules of international law applicable in armed conflict, with intent to betray that confidence”. Belligerents thus may not, for example, disingenuously accept a truce or announce their capitulation, feign injury or illness, or claim civilian or other protected status.
 In the next paragraph of Article 37, however, explicitly permits ruses as “acts which are intended to mislead an adversary or induce a person to act recklessly but which infringe no rule of international law applicable in armed conflict and which are not perfidious”. While this particular provision only pertains to international armed conflicts (IACs), ruses are likewise licensed in non-international armed conflicts under customary international law. But modern applications of misinformation or more accurately, disinformation call into question its reflexive characterization in IHL as a ruse for several reasons. First, while ruses are presented in source materials as being intended to mislead an “enemy” or “adversary”, disinformation campaigns during armed conflict today are instead often oriented primarily towards the civilian population. Under that obligation of IHL, Militaries can mislead their enemies on the battle field, but they cannot misguide or mislead the population in International armed conflicts.
In the next paragraph of Article 37, however, explicitly permits ruses as “acts which are intended to mislead an adversary or induce a person to act recklessly but which infringe no rule of international law applicable in armed conflict and which are not perfidious”. While this particular provision only pertains to international armed conflicts (IACs), ruses are likewise licensed in non-international armed conflicts under customary international law. But modern applications of misinformation or more accurately, disinformation call into question its reflexive characterization in IHL as a ruse for several reasons. First, while ruses are presented in source materials as being intended to mislead an “enemy” or “adversary”, disinformation campaigns during armed conflict today are instead often oriented primarily towards the civilian population. Under that obligation of IHL, Militaries can mislead their enemies on the battle field, but they cannot misguide or mislead the population in International armed conflicts.
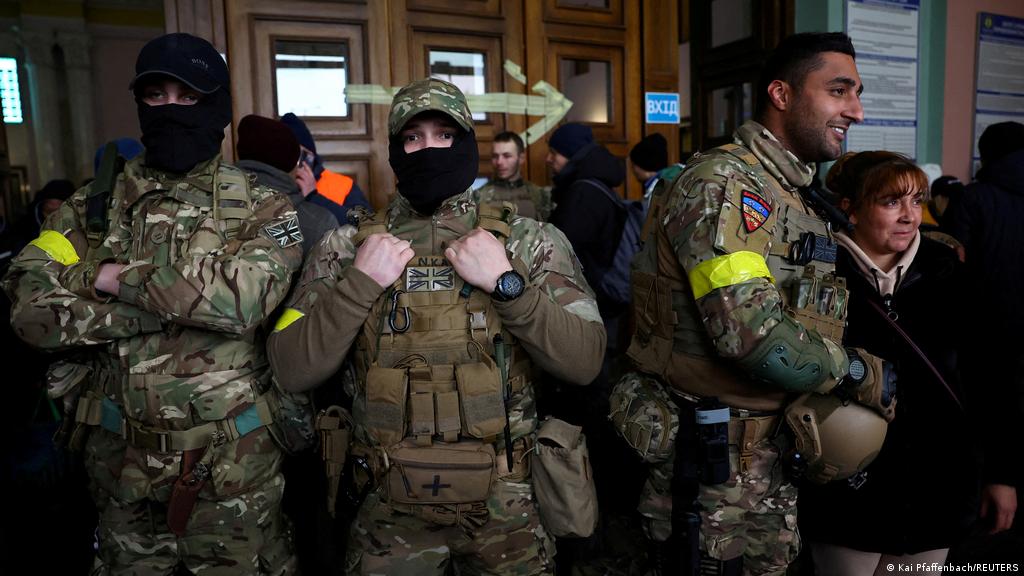

On 24, February 2022, Russia lunched a full scale war on Ukraine. Ukraine as compared to Russia is quite smaller in size having limited military resources, therefore it cannot hold their defence and doomed in a week. Ukraine as a favorite child to western democracies received lot of military aid to stop Moscow because they cannot put boots on the battle field for some political reasons. After the cold response from the NATO and the United States, Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy’s appealed, “Anyone who wants to join the defense of Ukraine, Europe and the world can come and fight side by side with the Ukrainians against the Russian war criminals.” Ukrainian authorities are welcoming the international individuals in their “international legion” brigade. Dozens of Americans, Canadians, and other foreigners are already trying to take up arms on the name of democracy and even they are motivated by the right wing white supremacy.
Moreover U.K. foreign secretary, Liz Truss showed her support for British nationals. The privatization of war and its support by the elected government is not a new concept. In Iraq and Afghanistan, US had used private militaries against enemies fighter to overcome their loses in the war. “Black water”, “New Century” and many more were the private militaries who got the contract over that period. From the perspective of state, private militaries are cheap and above the international law which can operate freely in the conflicted zone. It also reduce the cost of war and it also provide a way to politician to not stand accountable in front of people. The foreign fighters and private militias are often more useful in an insurgency and civil war, Ukraine may become like Afghanistan, Syria or Iraq. For guerrilla conflicts, the foreigners’ dedication is vital and their limited firepower is less of a disadvantage. The main problem in the privatization of the military is regarding the human rights violations, discrimination between combats and non-combat is very tough to make during conflicts, greed and revenge also dictate private militias to miss-use their power over civilians. In this scenario, rational thinking should be prevail in Ukraine war and international community should discourage such irresponsible privatization of war, and take some necessary actions to prevent foreign fighters to enter the Ukraine for the sake of innocent people. They should learn lesson from the distractive war of Afghanistan and Middle East, where private militaries and non-state actors were used to gain political objective by the parties in the conflict.

We are living in the digital era where media is playing a prominent role in our daily lives from individual to statecraft. Media has its own atmosphere which impacts on human minds. So, in that realm of the digital world, we cannot ignore the presence of digital media and its influence in politics.
Digital media is the main source of information from common to upper classes, when states and regimes controlling the flow of information. According to data provided by “Our World”, it is estimated that one in three people uses social media worldwide, more than 2.3 billion people out of seven billion use the social media to access information. The use of social media for manipulation is commonly increasing in different parts of the world which is quite evident. Many political and non-state actors use social media to proliferate their ideologies in general population. Their activities range from disinformation campaigns to rumors over transit options and hate speech around different groups. Social media is leading to overloaded distrust information, critical gaps as well as confusion over news and information.
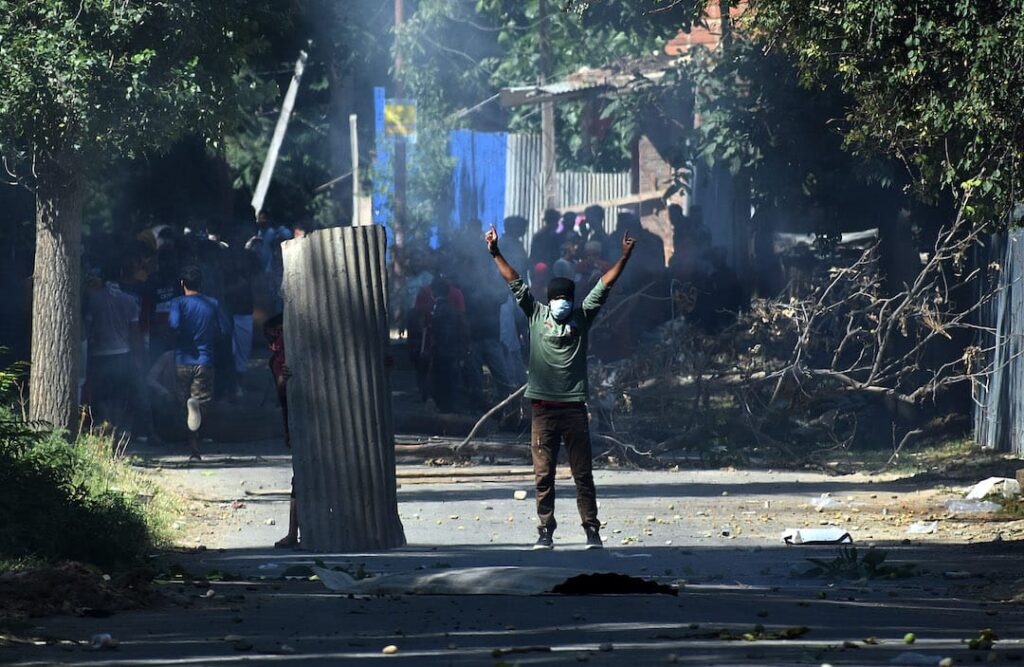
 In the context of conflicted areas, social activists, international organizations, independent news agencies use social media as a weapon to report human rights violation. State organized violence and mass killing highlights the stories of oppressed ones. In the region of Kashmir which is disputed territory between India and Pakistan. The social media have played an effective role during recent mass mobilization for “right to self-determination”. Indian administration imposed some serious censorship over digital and main stream media to cover up the human rights violations in the valley. Social media activism is posing a major challenge to the Indian state in Kashmir; most people are tending towards use of soft-power to empower their cause of right to self-determination.
In the context of conflicted areas, social activists, international organizations, independent news agencies use social media as a weapon to report human rights violation. State organized violence and mass killing highlights the stories of oppressed ones. In the region of Kashmir which is disputed territory between India and Pakistan. The social media have played an effective role during recent mass mobilization for “right to self-determination”. Indian administration imposed some serious censorship over digital and main stream media to cover up the human rights violations in the valley. Social media activism is posing a major challenge to the Indian state in Kashmir; most people are tending towards use of soft-power to empower their cause of right to self-determination.
Ground realities from conflicted area portrayed through digital media has helped international organizations, NGO’s and government institutions to pressurize the Indian occupation forces to stop violence. Frequent internet bans in Kashmir territory have been widely criticized by international organizations like UNO and Amnesty International. Many political analysts across the world as an arbitrary act to sabotage dissent and to serve as a form of ‘collective punishment’ for Kashmiri people in the region.

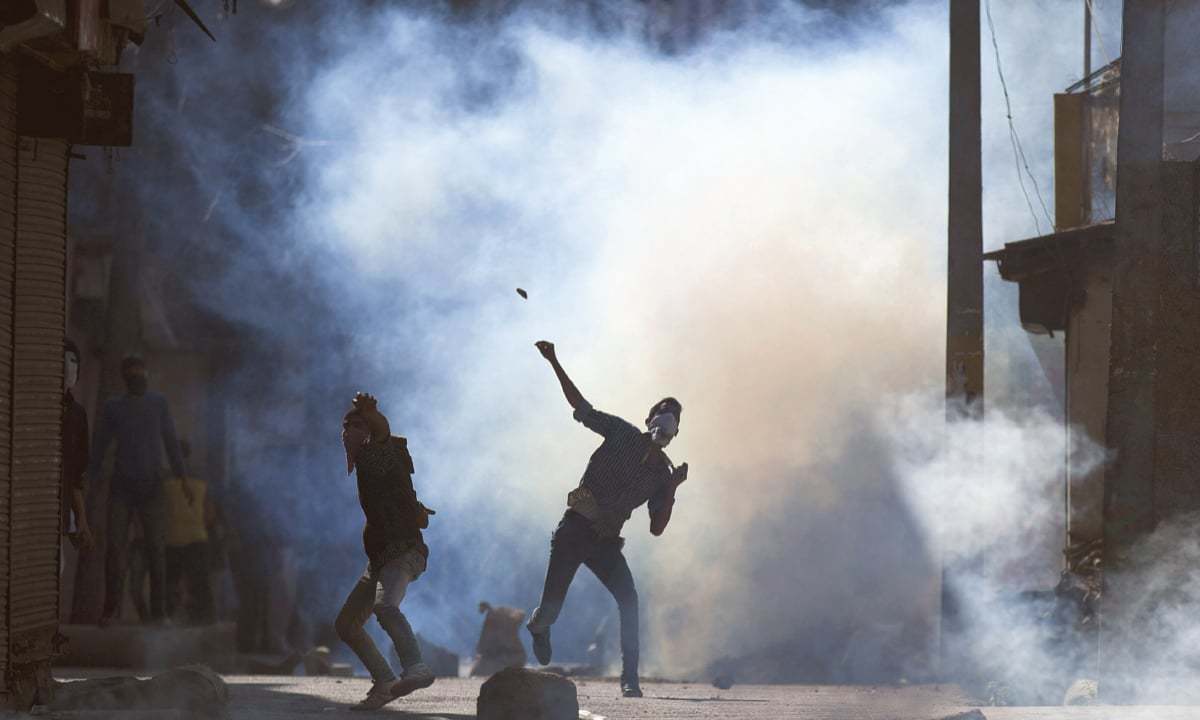
After the killing of Burhan Wani, a young social media activist with a fundamental ideological approach towards Kashmir movement, by Indian Armed forces inspired a whole generation of young people to raise their voices against Indian government and their atrocities in the region. This particular event and Burhan has become a symbol of both the youthful defiance on streets and the oppression of the Indian security forces by using Camera and Gun at the same time.
On August 5, 2019, India abrogated Article 370 and 35 A, which further more destabilized the valley of Kashmir. When the Indian government scrapped the region’s semi-autonomous status, and declared Kashmir as part of Indian union territory against all international and bilateral agreement with Pakistan, this created the political instability in the region and people started chanting on the streets against the unlawful act by the Indian Administration. In response to that, Indian authorities imposed a sweeping communication and internet shutdown in the region. The internet shut down continued for months, the longest internet suspension that took place in a democracy. According to an international organization “Access Now”, social media giants like Facebook, Twitter and YouTube joined hands with Indian government to remove the content related to Kashmir, which is projecting the freedom struggle of Kashmiri people. Kashmiri voices in the digital spaces through the frequent suspension of the accounts of artists, academics, and journalists based in and outside the disputed region, a move termed by experts as “inacceptable in free world”. Geeta Seshu, co-founder of Free Speech Collective group stated that, “Successive governments have censored and silenced voices of dissent in Kashmir for decades now but when social media companies do so too, it becomes all the more reprehensible.”
 Kashmiri activists and artists came with new ideas to cope up with this situation and initiated campaigns using the instrument of Music, Culture and Poetry to support Kashmiris against the oppression of India. On September 20th 2019, Kashmiri artists, highlighted the theme of “Resist to Exist” with the collaboration from British-Kashmiri artist Sumaya Teli and Kashmiri-American artist, Nouf Bazaz. Through the collaboration of artists, the event shared stories of the Kashmiri struggle against Indian occupation and militarization and for the right to Kashmiri self-determination. It went viral in different parts of the world, and help youth to understand the Kashmir situation and Indian mistreatment of Kashmiri people. In the recent six to seven years, we have seen, how digital media revolutionized the Kashmir Conflict and created the environment where young researchers and activists can access the information to understand the conflict and to advocate the worth of freedom for the next generations.
Kashmiri activists and artists came with new ideas to cope up with this situation and initiated campaigns using the instrument of Music, Culture and Poetry to support Kashmiris against the oppression of India. On September 20th 2019, Kashmiri artists, highlighted the theme of “Resist to Exist” with the collaboration from British-Kashmiri artist Sumaya Teli and Kashmiri-American artist, Nouf Bazaz. Through the collaboration of artists, the event shared stories of the Kashmiri struggle against Indian occupation and militarization and for the right to Kashmiri self-determination. It went viral in different parts of the world, and help youth to understand the Kashmir situation and Indian mistreatment of Kashmiri people. In the recent six to seven years, we have seen, how digital media revolutionized the Kashmir Conflict and created the environment where young researchers and activists can access the information to understand the conflict and to advocate the worth of freedom for the next generations.

In 2015, Iran signed a Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA) agreement, which is commonly known as “Iran Nuclear Deal”. The signatories of the deal were Islamic Republic of Iran and world powers including USA, UK, Russia, France, China and Germany ( P5+1) which refers to the five permanent members of United Nations Security Council (UNSC) and Germany. The main purpose of the agreement was to control Iran’s nuclear program, nuclear non-proliferation in order to curb the spread of nuclear weapons and technology in Iran as well as to ensure that nuclear technology is used only for peaceful and civilian purposes.
Here is the timeline of Iran’s nuclear program which starts from 1950s Iran was the first beneficiary and signed an agreement in 1957 with Washington. The first nuclear reactor was built in 1967 with the help of US. During 1970s, Iran expanded its nuclear plan to a greater extent, in this time Iran’s relationship with western countries deteriorated due to which west support for the Iranian nuclear project came to an end. In 1984, US Department of State listed Iran as state sponsors of terrorism and sanctions were imposed. Throughout the 1990s, US monitored the activities of Iran to look any kind of transfer of material and technology that could help in developing any conventional weapons. In early 2000s, covert nuclear program sites in Natanz and Arak for uranium enrichment were revealed by Iran to which International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) passed a resolution against Tehran to suspend its nuclear activities. Iran’s first domestically made satellite launched in 2009, which increased the concerns of the international community over the potential growth of ballistic missiles.
 Till 2014, “Two Track Diplomacy” was followed by the major powers as they encouraged Iran for diplomatic negotiations, at the same time sanctions were being imposed on Iran’s energy and finance sectors. All these events led to the nuclear deal, a landmark accord reached in 2015 which brought together the permanent members of UN Security Council and the European Union for a shared commitment. Under the deal, Iran dismantled much of its nuclear program and opened the nuclear sites for inspection, in return sanctions were lifted and Iran was allowed to make economic relations with the international community. Iran agreed to restrain nuclear activities and it was assured by US that no new sanctions will be imposed.
Till 2014, “Two Track Diplomacy” was followed by the major powers as they encouraged Iran for diplomatic negotiations, at the same time sanctions were being imposed on Iran’s energy and finance sectors. All these events led to the nuclear deal, a landmark accord reached in 2015 which brought together the permanent members of UN Security Council and the European Union for a shared commitment. Under the deal, Iran dismantled much of its nuclear program and opened the nuclear sites for inspection, in return sanctions were lifted and Iran was allowed to make economic relations with the international community. Iran agreed to restrain nuclear activities and it was assured by US that no new sanctions will be imposed.
When Donald Trump came into power in 2018, a unilateral American withdrawal from nuclear deal was observed and again sanctions in 2020 were imposed on Iran specifically on its oil sector for not acting in accordance with deal. However, the IAEA repeatedly corroborated that Iran has complied all the nuclear deal obligations. Other signatory members of Iran Nuclear deal objected the decision taken by US and said “United States cannot unilaterally invoke “snapback” sanctions because it withdrew from the JCPOA in 2018”. These members have interests in Iran because of its significant geostrategic location, also suggested by various analysts after JCPOA that it is a “roadmap for cooperation”. The nuclear deal was of great importance for all the stakeholders including; Iran, P5+1 as well as MENA countries. The prospects of the deal were to strengthen Iran’s position in the Middle East, economy, infrastructure, and political aspects. For EU, extensive trade and investment opportunities were predicted and the issues of concern like the nuclear program, regional security will be discussed with framework and negotiations. Despite of Washington’s isolationist policy, European Union has good relations and a unique approach towards Tehran.
On the other side, Russia did not follow the move of US. Russia was highly disappointed and slammed the decision by considering it as a blatant violation of international law and continued to maintain bilateral relations with Iran in political, economic and military areas. Since the US withdrew from the nuclear deal, Russia has become an advocate of the deal and has made active diplomatic efforts to induce its Western European signatories to resume economic relations with Iran despite US sanctions. The relationship between Russia and Iran is essentially based on geopolitical and strategic factors. The strategic relationship is mostly based on their shared objective in limiting US influence; Tehran is primarily concerned with the regional dimension while Moscow considers global perspective. The Russian leadership view Iran as a vital partner with whom it shares a number of objectives; who understands power dynamics and is ready to seek practical solutions where Moscow and Tehran’s interests diverge.
 The Joe Biden administration after coming to power in 2021 pledged to revive the nuclear deal to which Iran also agreed on a condition of indirect involvement, talks resumed in November in Vienna. Last month on 23rd Feb 2022, a European Union representative to talks said “We are nearing the end” over the success or failure of renewed Iran nuclear deal. The next day Russia-Ukraine crisis erupted, for the UK, US and EU have imposed sanctions on Russia’s oil, gas and financial sector, trade and travel restrictions also made, in response to that Russia has also banned exports. According to the participants of talks, the deal was on the verge of being finalized after a year of discussions. But, last-minute demands from Russia, one of the deal’s signatories, have threatened to undermine the efforts to revive JCPOA. Russia has said it wants assurance that Western sanctions imposed on Moscow will not prohibit Russia from doing business and military cooperation with Iran. The outcome of the current intensive discussions in Vienna aimed at restoring Iran’s 2015 nuclear deal with world powers and Iran’s relationship with Russia now has to be foreseen in coming days.
The Joe Biden administration after coming to power in 2021 pledged to revive the nuclear deal to which Iran also agreed on a condition of indirect involvement, talks resumed in November in Vienna. Last month on 23rd Feb 2022, a European Union representative to talks said “We are nearing the end” over the success or failure of renewed Iran nuclear deal. The next day Russia-Ukraine crisis erupted, for the UK, US and EU have imposed sanctions on Russia’s oil, gas and financial sector, trade and travel restrictions also made, in response to that Russia has also banned exports. According to the participants of talks, the deal was on the verge of being finalized after a year of discussions. But, last-minute demands from Russia, one of the deal’s signatories, have threatened to undermine the efforts to revive JCPOA. Russia has said it wants assurance that Western sanctions imposed on Moscow will not prohibit Russia from doing business and military cooperation with Iran. The outcome of the current intensive discussions in Vienna aimed at restoring Iran’s 2015 nuclear deal with world powers and Iran’s relationship with Russia now has to be foreseen in coming days.

The conflict between China and Taiwan dates back to the Chinese Civil War in 1949. China has territorial claims over Taiwan and considered it as a breakaway province that has to become a part of the People’s Republic of China (PRC) ultimately. However, the Taiwanese oppose the view and contemplate Taiwan as an independent state. The US have been a primary actor in the particular issue since the inception of civil war, even it was announced that no official position will be taken and two sides must resolve the issue peacefully. Initially, the US recognized Taiwan until 1978 after that “One China” policy was adopted by the US who laid the foundation of Sino-US formal diplomatic relations in 1979. But at the same time, non-diplomatic relations were maintained with Taiwan. In the same year, Taiwan Relation Act (TRA) was passed to support the island and govern policy toward Taiwan. The TRA affirmed US help for Taiwan to defend itself. For that purpose, the US deployed troops on Taiwan, kept selling arms, and also retained its nuclear weapons in Taiwan Strait. It is specified by the country that “Taiwan’s Future” is a risk to Western Pacific and is of utmost concern for the United States.
 Beijing’s policy towards Taipei is of deterrence, the goal is to stop Taiwan from formal independence, western support for Taiwan, and particularly US intervention. US policy towards Taipei is of “strategic ambiguity” in case of Beijing’s attack. Taiwan, a small island, yet it is of the utmost importance for China as well as the United States. On the basis of the geostrategic location of Taiwan in the Indo-Pacific region and to restrain the rise of China in global politics, strengthened military posture and influence in East Asia has shifted strategic objectives of US. The United States has been playing the “Taiwan Card” for the strategic rivalry with China. Apart from strategic, US have expanding economic as well as ideological objectives. Taiwan is the world’s largest chip manufacturer and the 10th biggest trading partner of Washington in the high-tech industry and semi-conductor production while supporting US economy with $600 Billion. Another strategic factor is that, when Taiwan will be under the jurisdiction of China, it would extend its missile ranges eastward by around 150 nautical miles. As a result, China would become the dominating force in the East China Sea, making it easier for Beijing to attack its rivals. US-China strategic competition and cross-strait relations are resulting in strong alignments among US and Taiwan.
Beijing’s policy towards Taipei is of deterrence, the goal is to stop Taiwan from formal independence, western support for Taiwan, and particularly US intervention. US policy towards Taipei is of “strategic ambiguity” in case of Beijing’s attack. Taiwan, a small island, yet it is of the utmost importance for China as well as the United States. On the basis of the geostrategic location of Taiwan in the Indo-Pacific region and to restrain the rise of China in global politics, strengthened military posture and influence in East Asia has shifted strategic objectives of US. The United States has been playing the “Taiwan Card” for the strategic rivalry with China. Apart from strategic, US have expanding economic as well as ideological objectives. Taiwan is the world’s largest chip manufacturer and the 10th biggest trading partner of Washington in the high-tech industry and semi-conductor production while supporting US economy with $600 Billion. Another strategic factor is that, when Taiwan will be under the jurisdiction of China, it would extend its missile ranges eastward by around 150 nautical miles. As a result, China would become the dominating force in the East China Sea, making it easier for Beijing to attack its rivals. US-China strategic competition and cross-strait relations are resulting in strong alignments among US and Taiwan.
 All the actors involved in the conflict have different perspectives over Taiwan depending upon their interests. When we look at the NATO’s objectives in China and Taiwan conflict, the European member countries of NATO have economic objectives that could be disrupted because of a military confrontation. US along with these NATO members has underscored the importance of Taiwan in terms of peace and stability in a joint statement. In opinion of China, Washington has destabilized the region with provision of weapons to Taiwan. Therefore, demands are being made by Beijing to withdraw its deployed troops in Taiwan while US has asked the former to stop proactive military activities in Taipei. This has increased the magnitude of rivalry between two states. Also, the tensions between Taiwan and China has reached the highest levels in past few years especially after 2016, when Taiwanese President held the office and rejected the Chinese territorial claim of Taiwan. Both China and America have potential to ignite military and economic war over the issue of Taiwan. For unification of Taiwan and “Greater China”, Beijing has a political strategy which involves a military component and US analysts see invasion as the only military option which pose a great risk of military confrontation. The international order will be in jeopardy after Taiwan war. If the war begins at Taiwan Strait, it is more likely that Taiwan would be a battlefront for the world’s two countries with most powerful military forces and will become Sino-America war than China vs. Taiwan. The conflict will affect the overall region that may turn into a war zone. Impacts will also be seen on global supply chains, financial and transportation links.
All the actors involved in the conflict have different perspectives over Taiwan depending upon their interests. When we look at the NATO’s objectives in China and Taiwan conflict, the European member countries of NATO have economic objectives that could be disrupted because of a military confrontation. US along with these NATO members has underscored the importance of Taiwan in terms of peace and stability in a joint statement. In opinion of China, Washington has destabilized the region with provision of weapons to Taiwan. Therefore, demands are being made by Beijing to withdraw its deployed troops in Taiwan while US has asked the former to stop proactive military activities in Taipei. This has increased the magnitude of rivalry between two states. Also, the tensions between Taiwan and China has reached the highest levels in past few years especially after 2016, when Taiwanese President held the office and rejected the Chinese territorial claim of Taiwan. Both China and America have potential to ignite military and economic war over the issue of Taiwan. For unification of Taiwan and “Greater China”, Beijing has a political strategy which involves a military component and US analysts see invasion as the only military option which pose a great risk of military confrontation. The international order will be in jeopardy after Taiwan war. If the war begins at Taiwan Strait, it is more likely that Taiwan would be a battlefront for the world’s two countries with most powerful military forces and will become Sino-America war than China vs. Taiwan. The conflict will affect the overall region that may turn into a war zone. Impacts will also be seen on global supply chains, financial and transportation links.
 The current ongoing war launched between Russia and Ukraine can also have an influence on China over Taiwan. Earlier, US intelligence chief stated; ‘’China’s interpretation of western reaction is being observed by Washington’’. Some experts have suggested that Ukraine crisis might encourage China to take military action against Taiwan, if it becomes necessary. President of US, Joe Biden has sent an extraordinary delegation of officials in wake of Ukraine-Russia war to warn China and declared Washington’s strong support for Taiwan. Meanwhile, the Chinese ambassador to Washington has also alerted US of military confrontation risk over Taiwan. The increasing tensions between Sino-US relations and cross-strait relations can be a flashpoint of military confrontation.
The current ongoing war launched between Russia and Ukraine can also have an influence on China over Taiwan. Earlier, US intelligence chief stated; ‘’China’s interpretation of western reaction is being observed by Washington’’. Some experts have suggested that Ukraine crisis might encourage China to take military action against Taiwan, if it becomes necessary. President of US, Joe Biden has sent an extraordinary delegation of officials in wake of Ukraine-Russia war to warn China and declared Washington’s strong support for Taiwan. Meanwhile, the Chinese ambassador to Washington has also alerted US of military confrontation risk over Taiwan. The increasing tensions between Sino-US relations and cross-strait relations can be a flashpoint of military confrontation.

Pak-U.S Relations Flashbacks:
In order to analyze the current Pak-U.S relations, there is a need of shedding a light upon the historical background of their relations.
Pakistan is the country that holds the great geostrategic importance. Right after the independence, it faced security and economic issues. Earlier, U.S was against the creation of Pakistan and divided India but later on, Pakistan and U.S did establish ambassadorial relationship. During the cold war era, Pakistan and U.S foreign policy revolved around military-diplomatic relations and defense policies. In this war of capitalists vs. communists, Pakistan chose U.S block rather than the communists Soviet’s block because it suited the Pakistan’s ideology, democratic ideas of the leaders and its economic interests. U.S foreign policy has always involved the idea of establishing its ideology like democracy or capitalism in the states. So, it did the same in the cold war and allied with Pakistan to increase its sphere of influence in the South Asian Region. India was pro Soviets and Pakistan was pro-U.S.
Since the 1950s, each side was using the other to enhance its own agenda that significantly affected each other’s interests. The goals of the Pak-US relationship were only partially served. U.S had also put sanctions on Pakistan. For example, after 1965 Pak-Indo war, U.S put sanctions on Pakistan and there was an economic collapse in Pakistan. Pakistan also fought along with U.S against the Soviet Union in Afghanistan. After the Soviet’s withdrawal from Afghanistan, U.S imposed nuclear sanctions on Pakistan as well. In the post 9-11 era, Pakistan was also blamed for terrorism but then, joined hands with U.S to fight against terrorism. U.S interests lied in Pakistan in order to fight the war on terror in Afghanistan and it was also in Pakistan’s interest to have peace in its neighboring country or else, there would be no peace in its own region.
Fast forward, there have always been ups and downs in their relationship.
Analysis:
Pakistan-U.S relations have been much better if they had not solely relied on security threat perceptions and strategic interests. There would have been a sustainable relationship among them if the economic factor was involved. By economic factor, it does not mean the financial aid provided by the U.S to Pakistan, but the economic diplomacy that is among China and Pakistan. Projects like CPEC and BRI have and will strengthen the relationship between Pakistan and China for the long term. This is because of the involvement of the economic interests of both countries.
Right after the U.S withdrawal from Afghanistan in 2021, zero diplomacies in Pak-U.S relations has been observed. The role of Pakistan in the ‘’U.S-Afghan Taliban negotiations’’ process, and the sacrifices made in ‘’war on terror’’ have also not been acknowledged by the U.S. It seems like there is no common interest left between both of the states that can bind both of them together.
 Keeping good relations with Pakistan had been beneficial for U.S since it could contain the economic influence of China. Now, when China has involved Pakistan and many other South Asian regions in its economic activities like CPEC and BRI, still, no counter-strategy is visible from the U.S’s side. There is a big possibility that U.S foreign policy is focusing on the other regions (like the Middle East, Europe or Central Asia) and will shift again towards South Asia. This fact cannot be denied that countering China’s economic hegemony in the top priority of U.S’s Foreign policy and it might be secretly working to counter this. China is filling the vacuum left by U.S in different regions for example, RCEP which is Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership is the first multi-lateral free trade agreement that aims to create a consolidated market for the 10 member countries and their trade partners. RCEP in an agreement signed between 10 ASEAN states and also China, Japan, South Korea, New Zealand, Australia are signatory states. These countries contribute 29 percent to the world’s economy. This agreement has the potential to provide liberal facilities and a competitive investment environment in the Asia-Pacific region. China joined RCEP in response to the US-led Trans-Pacific Partnership. Also, COVID 19 led the countries to join this economic emancipation. This will extend the China’s influence in Asia-Pacific, and it is perceived that this is how it is countering US strategic pivot to Asia. RCEP is seen to be a political victory and not just an economic victory. U.S political influence in this region can also decrease. RCEP also gives an opportunity in wake of the decoupling of China. This may improve China’s perception and relation with Southeast Asian nations. America exports around 5.3 billion goods to Japan but it will now decrease since Japan will have better access to Chinese firms. RCEP impels U.S to respond to geopolitical primacy in the region. India did not participate in RCEP because according to them their local economy will be affected but on the other hand, it will also affect India’s look East policy. India can however collaborate with U.S more. CPEC and RCEP will have a linkage. It can also create economic opportunities for Afghanistan. Pakistan will have stronger relations with China. This will create two blocks “Indo- U.S” and “Pak- China” block. According to the US president Biden, America has to align with other democracies.
Keeping good relations with Pakistan had been beneficial for U.S since it could contain the economic influence of China. Now, when China has involved Pakistan and many other South Asian regions in its economic activities like CPEC and BRI, still, no counter-strategy is visible from the U.S’s side. There is a big possibility that U.S foreign policy is focusing on the other regions (like the Middle East, Europe or Central Asia) and will shift again towards South Asia. This fact cannot be denied that countering China’s economic hegemony in the top priority of U.S’s Foreign policy and it might be secretly working to counter this. China is filling the vacuum left by U.S in different regions for example, RCEP which is Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership is the first multi-lateral free trade agreement that aims to create a consolidated market for the 10 member countries and their trade partners. RCEP in an agreement signed between 10 ASEAN states and also China, Japan, South Korea, New Zealand, Australia are signatory states. These countries contribute 29 percent to the world’s economy. This agreement has the potential to provide liberal facilities and a competitive investment environment in the Asia-Pacific region. China joined RCEP in response to the US-led Trans-Pacific Partnership. Also, COVID 19 led the countries to join this economic emancipation. This will extend the China’s influence in Asia-Pacific, and it is perceived that this is how it is countering US strategic pivot to Asia. RCEP is seen to be a political victory and not just an economic victory. U.S political influence in this region can also decrease. RCEP also gives an opportunity in wake of the decoupling of China. This may improve China’s perception and relation with Southeast Asian nations. America exports around 5.3 billion goods to Japan but it will now decrease since Japan will have better access to Chinese firms. RCEP impels U.S to respond to geopolitical primacy in the region. India did not participate in RCEP because according to them their local economy will be affected but on the other hand, it will also affect India’s look East policy. India can however collaborate with U.S more. CPEC and RCEP will have a linkage. It can also create economic opportunities for Afghanistan. Pakistan will have stronger relations with China. This will create two blocks “Indo- U.S” and “Pak- China” block. According to the US president Biden, America has to align with other democracies.
This all has affected U.S-Pakistan relations and it has been assessed that Pakistan has close economic ties with China and there is a strong bond. So in order to contain China’s economic expansion globally, America is looking towards the other regions. China has very much a Pro-Russia policy. Keeping that in view, Pakistan’s stance has remained neutral in the Ukraine-Russia war Even though Ukraine did not get enough support and defense from U.S in the Russia-Ukraine war because of the U.S vested interests in Russia but still Pakistan has been criticized for remaining neutral, the irony! This has further complicated US-Pakistan relations. If we analyze the current foreign policy of Pakistan, there is a lot of focus on the economic diplomatic relations other than China as well. For example, Engage Africa Policy, Strategic Engagement Plan with European Union and Strategic Economic Framework with Turkey. Pakistan and China have also involved Russia in the BRI project. Pakistan has no such economic diplomatic relations with U.S but still, it would never be an easy decision for the United States to entirely abandon or fully engage Pakistan.

UKRAINIAN REFUGEES; IMPACT ON EUROPEAN UNION
BY HAMNA SEYYED
The crisis comes unexpectedly and is often unforeseen. Similarly, the Russian and Ukrainian forces’ abrupt war on 24th February 2022, was unexpected and left Ukraine in a chaotic situation. The destruction caused by the military invasion created unlivable circumstances for the Ukrainians and they had to leave. Therefore, it led to conflict-induced migration and the displacement of the Ukrainians. Once again Europe is dealing with the refugees as it did back in 2015. As per the United Nations, 100,000 Ukrainians are already being displaced.
For the time being, Refugees are being welcomed by the European Union states like Poland, which plans to host up to 1 million Ukrainians, as well as Romania, Hungary, Slovakia, and Moldova, where 4,000 Ukrainians came, are among the host countries. Yet, these countries are presently unprepared to stop the influx of refugees expected to arrive on their borders in the coming weeks. Hosting refugees is not an easy task at all. The major receiving countries in Central Europe can simply lack the capacity to address such needs on a large scale and over a long period. Conflict-Induced Migration is supposed to be temporary but the migrants or refugees can only be sent back once the conflict from their homeland gets over but the situation does not seem to get fine in Ukraine. Ukrainians’ needs range beyond the supply of temporary food, clothing, and shelter to get them through. They are at risk of being evacuated for a longer duration, which requires institutional pathways to legal status, reintegration services, housing, education, and healthcare. Refugees also require mental and social rehabilitation. Living in the era of the pandemic, they also require vaccination against Covid-19. Not only this, but European Union states still have to do a lot more for them, it will entail creating a regional resettlement plan and ensuring that overpopulation does not occur. Ukrainians may stay in the EU for up to three months without a visa, but it’s uncertain what sort of legal status they will have further than that. That has to be handled as well. The refugee crisis in Ukraine provides Europe with not only an important opportunity to prove its humanitarian values and commitment to the international refugee protection regime but it also offers a critical interesting perspective that now it is a challenge for Europe that whether it will be able to embrace the humanist spirit of the ‘’1951 Refugee Convention’’ or not. All the European states have different systems that they follow but, it will be mandatory for all member states to apply the provisions of this Convention. According to Article 3 of the Convention, ‘’The Contracting States shall apply the provisions of this Convention to refugees without discrimination as to race, religion or country of origin.’’

The best-case scenario can be that the violent conflict transforms and the pull factors in Ukraine shall be created so the refugees voluntarily return to Ukraine. The worst-case scenario can be analyzed in a way that if the conflict prolongs, the refugees have to stay for a longer period in the European Union states. This will be challenging to tackle. As a refugee or the conflict-induced migrant is the one who is coming from the conflict zone and brings a lot of grievances along with him, survival will always remain the priority and he will fight for it to an extent. If the refugees are not taken proper care of by the host states, the threat of host-stranger conflict can arise. It has been assessed that the refugees often have a cut-throat policy. Refugees can pose a threat to the national security of the states and their ability to govern. One of the examples of the refugee issues is of Afghan refugees in Pakistan. Who knew that the conflict in Afghanistan will remain protracted? Pakistan is facing a refugee crisis now. We live in the world of globalization and it has both, advantages and disadvantages. Pakistan’s culture and security did get affected by the Afghan refugees. The Refugees create an economic burden in the host states and because of this instability can be caused. Refugee identity crises have also seen to emerge in the case of many refugees throughout history. Refugees can pose a threat to a state’s sovereignty. Furthermore, the security issues like cross-border terrorism, drug trafficking, and illegal trade activities cannot be neglected. The root causes of the refugee’s problems have to be addressed and in the case of Ukrainian refugees, European Union states that are dealing with the refugees shall play a diplomatic role in terms of the Ukraine-Russia war. It will not only help the refugees but the European Union itself as well. European Union needs to be proactive and adopt policies for the refugees for the short, as well as a longer period of time with United Nations’ assistance.

The Houthis have a complex relationship with Yemen’s Sunni Muslims. The movement has discriminated against Sunnis, but also recruited and allied with them. Under the leadership of Hussein Badreddin al-Houthis, the group emerged as an opposition to former Yemeni president Ali Abdullah Saleh, whom they charged with massive financial corruption and criticized for being backed by Saudi Arabia and the United States.
The Houthi movement attracts its Zaidi-Shia followers in Yemen by promoting regional political-religious issues in its media, including the overarching U.S. Israeli conspiracy theory and Arab “collusion”. In 2003, the Houthis’ raised a slogan, “God is great, death to the U.S, death to Israel, curse the Jews, and victory for Islam”, and it became the group’s trademark. Houthis officials, however, have rejected the literal interpretation of the slogan. Iran is widely accused of backing the Houthis, a Zaydi Shiite movement that has been fighting Yemen’s Sunni-majority government since 2004. The Houthis took control of the Yemeni capital Sanaa in September 2014 and continued on towards Aden, Yemen’s largest city. In response to Houthi advances, Saudi Arabia and other Arab states launched a military campaign in March 2015.
Recently, The Houthi armed group has fired artillery and ballistic missiles indiscriminately into populated areas of Yemen’s Marib governorate resulting in civilian casualties, including women and children, and causing a new wave of civilian displacement. And now Houthi rebel attack on the Saudi Arabian town of Jizan resulted in two casualties and seven injured. The Houthi–Saudi Arabian conflict is an ongoing armed conflict between the Royal Saudi Armed Forces and Yemeni Houthi forces that has been taking place in the Arabian Peninsula, including the southern Saudi regions of Asir, Jizan, and Najran, and northern Yemeni governorates of Saada, Al Jawf, and Hajjah since the onset of the Saudi Arabian-led intervention in Yemen in 2015. On December 7, 2021, Reuters reported that the Saudi-led coalition bombed military targets in the capital Sanaa after the Iran-aligned Houthis launched ballistic missiles and armed drones into Saudi Arabia.
What is happening in the conflict now?
As the war has dragged on, Houthis have stepped up the boldness of their attacks on Saudi Arabia. Using drones and missiles, the Houthis have launched attacks on Saudi airports, oil facilities and military sites.
While Houthi attacks have failed to cause massive devastation, they have been enough to rattle global oil markets. Houthi attacks on Saudi Arabia have more than doubled this year compared to last year. CSIS records 78 Houthi attacks per month this year on Saudi Arabia, compared with 38 a month in 2020.
In Yemen, there is much criticism of the Saudi-led coalition’s attacks for targeting civilians in one of the world’s poorest countries. More than 80% of the population of 30 million requires food assistance. Estimates on the number of fatalities caused by the conflict vary widely, though at least some 130,000 have been killed over the course of the conflict. By contrast, the UN estimates the conflict will have claimed 377,000 by the end of the year, both through the direct and indirect consequences of war, such as disease and starvation.