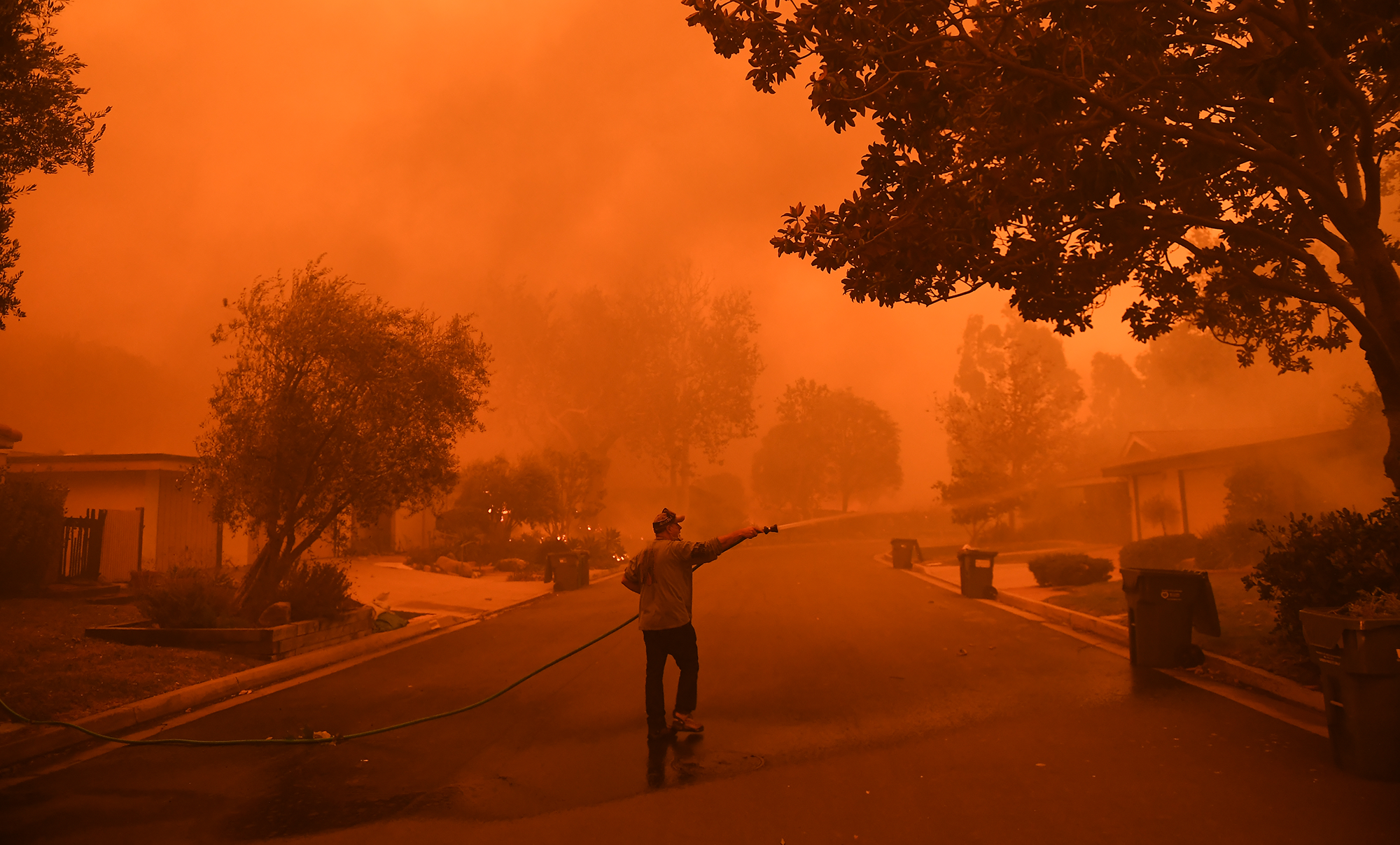
The Scorching Europe!
Introduction
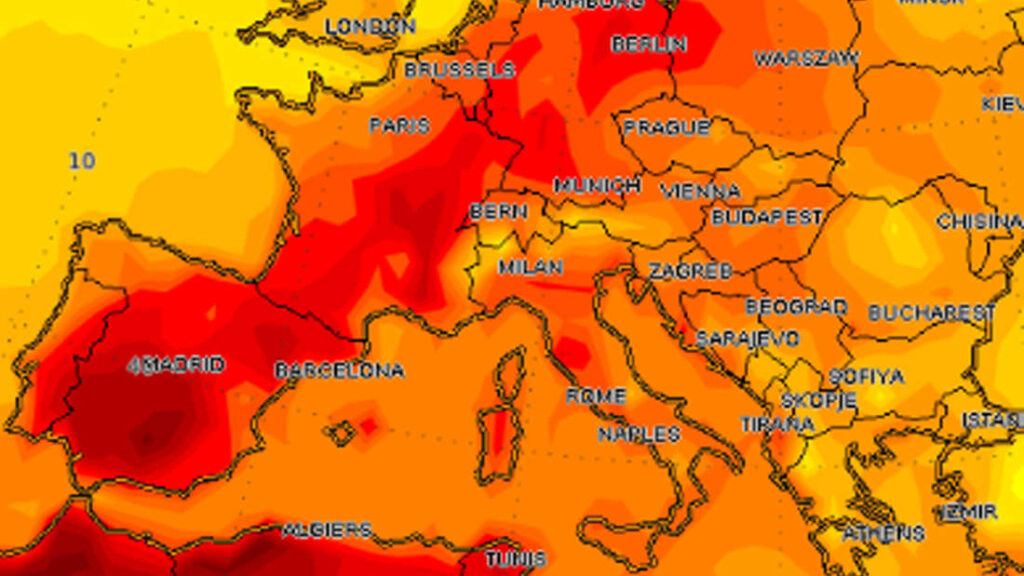
Europe is witnessing extreme heat waves for the very first time which has clutched the whole region by an intense increased temperature. The record breaking temperature has triggered wildfires that have spread over a vast area of nearly 27,000 acres due to which authorities are struggling to control the situation. Almost 19 European countries are still in extreme danger of forest or wildfires forecasted by European Forest Fire Information System. The railway and the transit systems have been destroyed badly in most parts of the region. The heat waves are increasing significantly more than ever in Europe and the negative trend is said to be continued by 2060 as per stated by the United Nations. Recently, in June, major countries of Europe like France and Portugal experienced drought and now the region is in severe crisis again. More than 31,000 people have been evacuated in France and 659 deaths have been reported in Portugal within a week, and alone in Spain, more than 500 people have died as a consequence of existing calamity. The rapidly changing global weather patterns in the form of current heat waves have not only affected Europe but also the United States and parts of China. The United States referred heat waves as the deadliest disaster and almost 600 people died as a result per year from 1999 to 2009. This year China observed highest temperature over 42 degrees Celsius causing death causalities. The spurring death toll is alarming and demands effective measures for the safety and protection of the people.
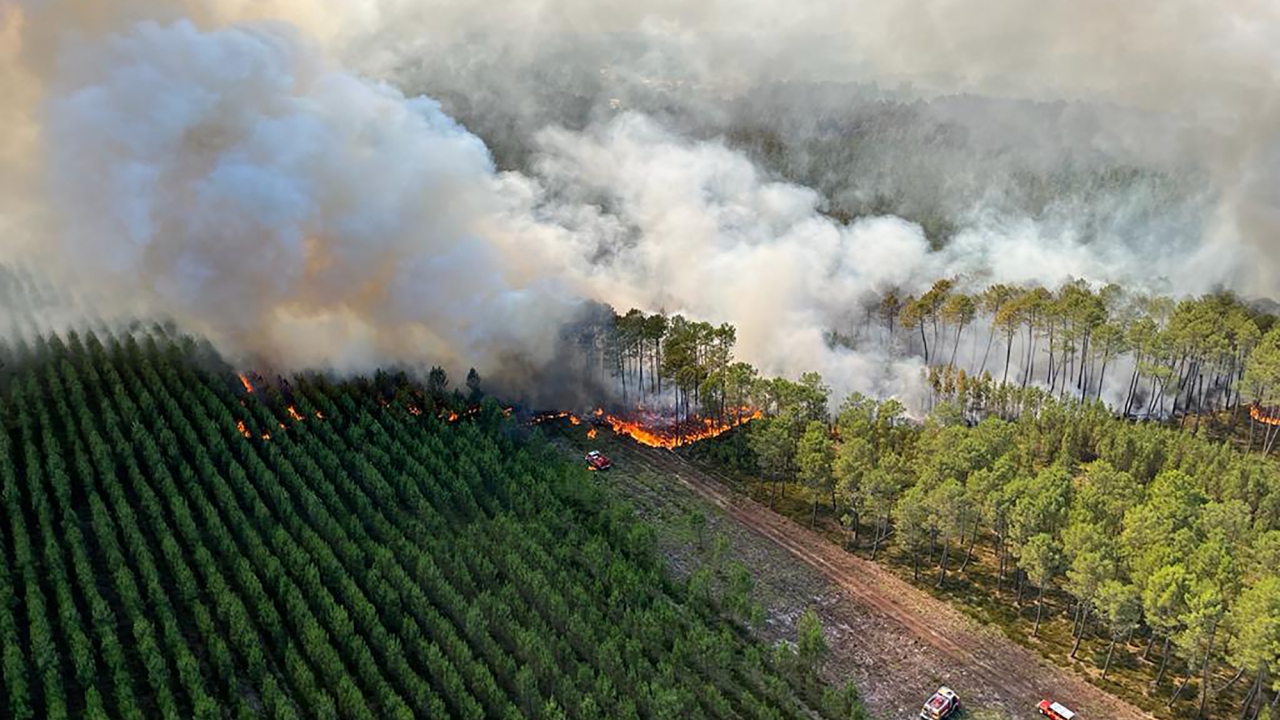

Climate Change and Heat Waves
Climate change is being contemplated as the root cause of the crisis and is a major driving force behind record-breaking and extreme heat waves. Heat waves are becoming more frequent and hotter due to climate change. The United Nations international panel i.e. Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) has concluded that this is the case for the majority of the regions. Experts have also attributed raged heat waves in Europe to uncheck human activities, since the start of industrialization, greenhouse gas emissions have increased global temperatures by around 1.2 degrees Celsius. It means that the average temperature of the Earth is increasing with the passing time which can create more worsening circumstances in the future in comparison with what all the regions are going through now. Since the base is getting warmer, extreme heat events can reach further higher temperatures and exacerbating dry conditions. Heat waves can have impacts on the livelihoods of people specifically marginalized sectors of society. Also, it will increase poverty, political instability and social tensions as well as food security will also be threatened as it have witnessed from South-Asian countries including Pakistan and India. But unfortunately, it is a dilemma that heat waves are not getting due attention of the concerned and responsible stakeholders to deal with the issue.
President Joe Biden’s Plan for Climate Change
The rising threat has been underlined by skyrocketing summer temperatures, with 100 million Americans currently under extreme heat warnings and devastatingly hot circumstances affecting anguish across the Europe has resulted in Joe Biden’s revival of Climate Agenda. On 20th July, while announcing a total of $2.3 billion to assist develop US infrastructure that can resist global disasters, Mr. Joe Biden said “the health of our citizens and our communities is literally at stake, our national security is at stake and our economy is at risk. So we have to act”. He added “Climate change is literally, not figuratively, a clear and present danger”.

Conclusion
Climate change is such an important issue that it should be identified as a concern of national security. The statement by President Biden shows the importance of climate change which is posing serious threats to a country’s traditional and non-traditional security. The climate has changed and will continue to change; there is a need of taking serious steps to deal with the concerned issue. It can be done by creating innovation in the existing course of action for adaptation, to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and tackle with the issues of global warming in an efficient manner at local, national, and international levels. Here the role of developed nations and the international community is crucial in terms of developing countries, as they are more vulnerable to the effects of climate change, policies must be designed in a way that proves a source of relief for them. The current situation of Europe should be considered as a wake-up call by all the countries and stakeholders to make an effort not only to safeguard planet Earth but the people of planet Earth as humanity comes first and should be the top priority.


