Blue Economy: A Comprehensive Analysis

Blue economy or blue growth as a concept came from a book written by Gunter Pauli. It is a relatively new concept that internationally came to light in 2012. It refers to strategic and sustainable use of marine resources for the development of the economy and the well-being of human beings. It offers a green approach to meet the aspirations of mankind. Blue economy involves the integration of ocean economy development with the principles of social inclusion, environmental sustainability and innovative dynamic business models such as the creation of environment-friendly infrastructures in the oceans.
A sustainable blue economy is very important because the sectors involved in the oceans, coasts and maritime environment are so diverse that if one industry goes for it exploits it and makes a lot of money it can destroy other industries. Thus, it is very important that a balance is created and sustainable development is maintained because particularly environmental tourism and nature tourism which are very large areas of those industries at the moment and particularly the coastal regions can be threatened. So, investment is needed in sustainable solutions and quick gains must be discarded in the favor of long-term goals. We should make sure that we responsibly use our shared resources, for both our present and future generations.

SIGNIFICANCE OF BLUE ECONOMY
There are countless benefits that we gain from the oceans in our daily life but we do not realize it. Oceans contribute about 3-5% of global GDP. They are a vital source of our food, annually fishing industry alone generates $80 billion. Oceans two biggest economic benefits are trade and employment which have always led to the exploitation of oceans. According to an estimate of 2010, blue economy added $ 1.5 trillion to world GDP while it directly employed 31000,000 individuals. Whereas, in 2016 according to FAO estimate fisheries and aqua culture involved 59.6 million people. Hence it represents an immense employment sector around the world whether directly or indirectly even in Europe alone blue sector offers 3,362510 jobs in 9 different sectors. About 90% of world trade takes place through oceans. Blue economy drives socio-economic benefits for present and future generations. Major states realized the importance of blue economy and engaged in activities to realize this idea for instance World Bank has initiated a program with name ‘PROBLUE’ to explore the opportunities of blue economy and ways for renewable and sustainable development of this economy.
OPPORTUNITIES
Sea and inland waters give noteworthy advantages to humankind. But keeping in view the current environmental degradation, this crucial asset is being deteriorating quickly with overfishing, contamination from land-based sources and overconsumption. Consequently, harnessing the maximum capacity of the seas and inland waters require policies and programs that are ecologically, socially and economically sustainable. There is a wide accord that Blue Economy can satisfy the necessities of increasing global demand for resources. This has been emphasized by many international forums, for example, OECD, UNEP and FAO. Few of the opportunities that can open up new avenues in blue economy are Marine Aquaculture, Marine Transport, Offshore wind energy, Offshore oil, Bio prospecting and Marine Tourism.
 SCOPE OF BLUE ECONOMY FOR PAKISTAN
SCOPE OF BLUE ECONOMY FOR PAKISTAN
Pakistan has marine area of 290,000 square km which makes up to 36.4% of the country’s territory. If the maritime area of Pakistan were a land piece, then it would be a little greater than Punjab province. This tells that Pakistan has blessed blue economic zone. The all-year functional seaport of Karachi and Port Qasim and world’s deepest port Gwadar with its strategic location add more to its significance. Despite all this, unfortunately, Pakistan suffers from what we call sea blindness. Some of the prospects for blue economy in Pakistan are discussed in the following paragraphs.
Pakistan’s multibillion-dollar CPEC project is being hailed as a watershed moment in the country’s blue growth. The CPEC is regarded as the jugular vein of China’s multitrillion-dollar BRI initiative. Moreover, Pakistan’s blue economy can greatly benefit from energy production from its seas and coast. One form of energy called tidal energy is gaining great interest. Utilizing this energy could be a renewable source of energy for its coastal cities of Gwadar, Karachi etc. Pakistan’s National Institute of Oceanography (NIO) in 1988, identified 17 coastal creeks for tidal energy. Similarly, wind energy near coastal areas, especially Balochistan are plump with strong winds. A survey identified an 18 MW energy potential on 1 km of land near the coastal belt.
It is well known that 80% – 90% of the world’s trade passes through the oceans. In the case of Pakistan, estimates put it at an astounding 95%. The shipping industry of Pakistan makes only $183 million. Compared to our South Asian neighbors, India makes $5.6 billion and Bangladesh makes $6 billion. If Pakistan inducts more ships and bridges the gap, a vast potential is present to decrease cost of imports as well as employ more Pakistanis and earn more money into the exchequer.
Ports in Pakistan are plenty but the main two ones are Karachi and Gwadar. Most of Pakistan’s trade passes through Karachi, but development of Gwadar port under CPEC has been a game-changer. Gwadar lessens the distance from more than 10,000 km to 2000 km – 3000 km. Soon afterwards, the rest of Chinese trade will go through Gwadar and Pakistan can profit greatly from all the traffic and tax.
Moreover, according to reports, we earn $100 million from our ship-breaking yards meanwhile the potential stands at $3 billion. The main issue lies with our Gadiani ship-breaking yard. Its Pakistan’s main and major ship-breaking yard, however, it is plagued with accidents, fires and deaths every few months. Low wages, poor equipment, government negligence and bad conditions pave way for an inefficient and danger prone environment. The money should be diverting to Gadiani ship-breaking yard’s upgradation and infrastructure so that Pakistan can become a top ship-breaking nation.
Pakistan’s 990 km coastal belt with a 320 nautical mile ocean claim covering 290,000 square km has a variety and excess of fish and marine life present. The government needs to tap this industry as it will prove effective for exports and domestic sales as well.
When talking about marine tourism, Pakistan must take inspiration from countries like Maldives, Sri Lanka, Philippines to develop the God gifted beautiful beaches and islands. According to experts, the total potential stands at $5 Billion for Pakistan.
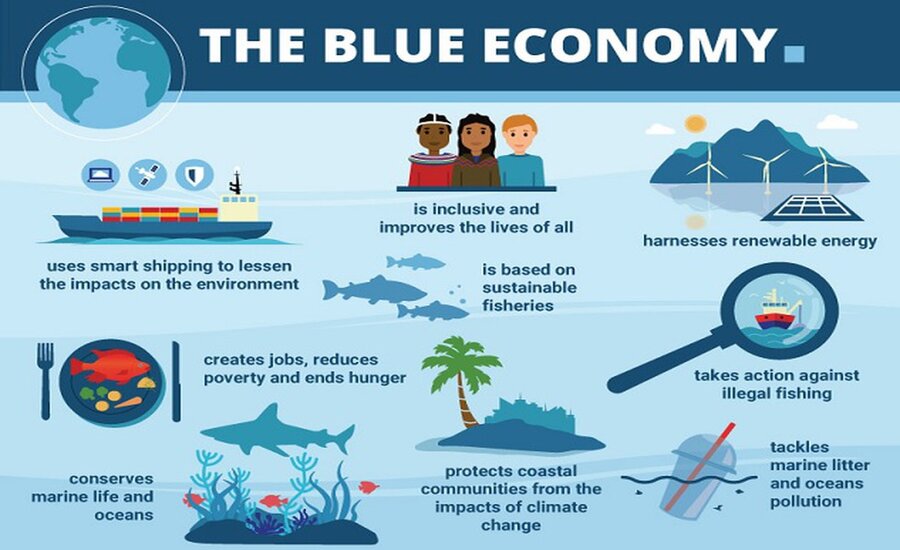
Conclusion:
The political elite in Pakistan must drive their focus towards blue economy and show strong commitment and seriousness to this sector. Pakistan must invest in both intellectual and physical resources as well as needs to take ironclad measures. Challenges in this path such as poor infrastructure, red tape inside the system, bureaucratic bottlenecks, regional instability, particularly a severe law and order situation in Balochistan, and a lack of cooperation between departments and ministries must all be addressed.

 Other emerging powers:
Other emerging powers: