The Elevating Role of SCO: Opportunities and Challenges for Pakistan

Introduction
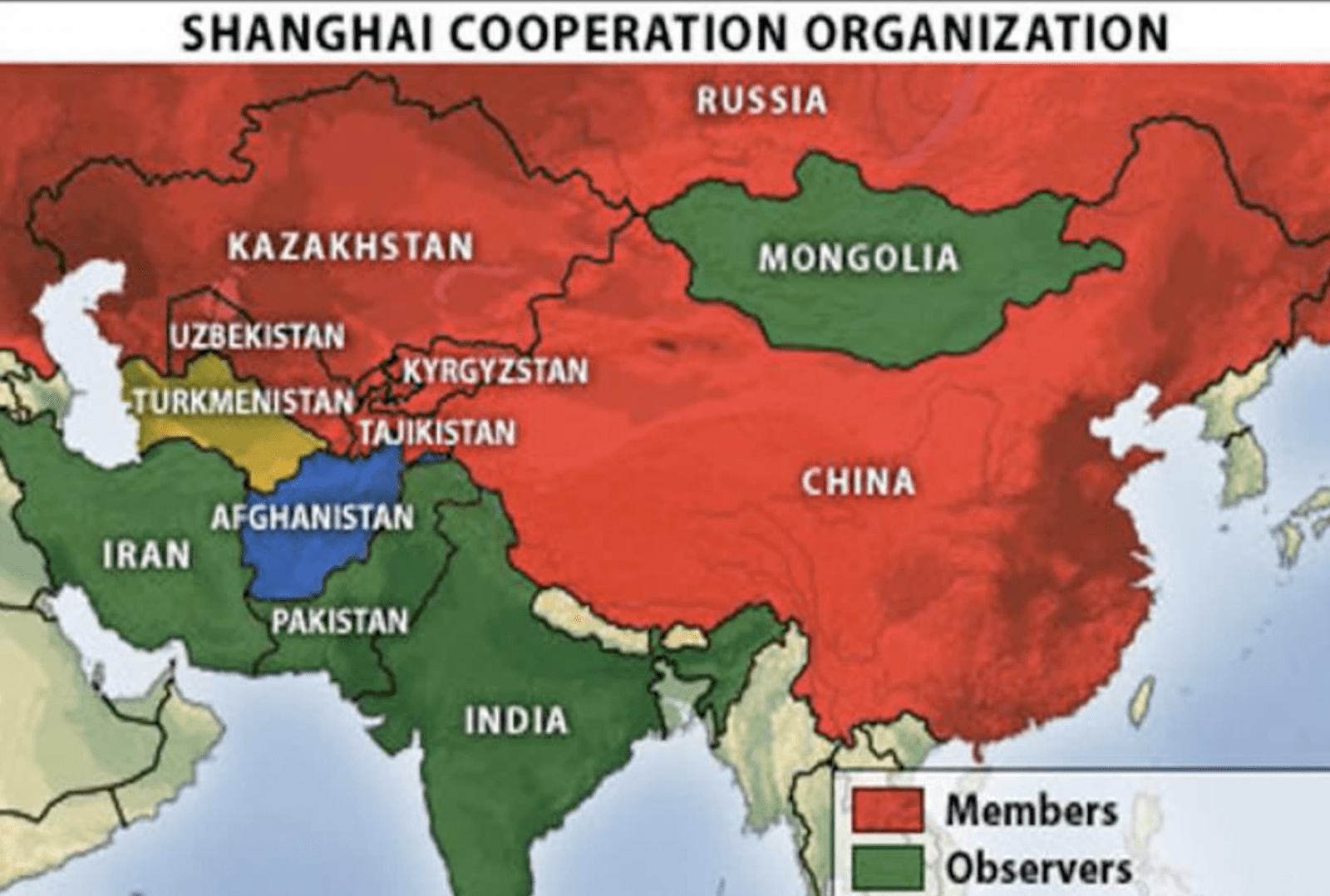
The Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO) has become a strategically important organization in the ever-changing world of international relations. The SCO’s activities have gained considerable attention as the organization has advanced significantly and is now a crucial component of the contemporary international political and economic world order. The SCO is demonstrating global aspirations by increasing the number of its members and attempting to exert its influence in regional and global issues. When the SCO was first established in 2001, its members were China, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Russia, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan. Its reach has grown significantly over time, and it currently counts Pakistan, Iran, and India as full members. Afghanistan, Belarus, and Mongolia are also observers, and Armenia, Azerbaijan, Cambodia, Nepal, Sri Lanka, and Turkey are “Dialogue Partners.” The SCO has expanded significantly with the membership of Saudi Arabia and the signing of memorandums with Qatar and Egypt.
Significance of SCO
Collectively, SCO countries cover a sizable portion of Asia, account for almost 30% of the world economy, and 40% of the population of the globe. The SCO has a large membership, which highlights its potential as a strong regional organization and a stabilizing force in the Eurasian continent. The goals of SCO are to advance collaboration, strengthen member state ties, maintain security and stability in the region, and push for a “new, democratic, just, and rational political and economic international order.” Promoting trade and economic cooperation is one of the organization’s main objectives. The primary cause of SCO’s importance in the region is the wealth of its resources. About half of the world’s known uranium deposits, 25% of the world’s oil reserves, more than 50% of the world’s gas reserves, and 35% of the world’s coal reserves are found in the current SCO member states. The region is also highly capable in production of food and technological advancements.
Pakistan and SCO: Opportunities and Challenges
Pakistan joined the SCO in June 2017, before that it benefited from the position of SCO Observer State from 2005 to 2017. Pakistan has had a long-standing relationship with SCO member states due to shared historical, cultural, civilizational, and geographical ties. Pakistan’s active engagement in SCO indicates its strong interest in regional peace, stability, and socioeconomic development.
Economic Cooperation and Connectivity
The SCO provides a venue for Pakistan to strengthen its regional economic linkages and cooperation in critical areas such as trade, investment, energy, innovation, transportation and connectivity. SCO is a key venue for moving Eurasian connectivity forward. Pakistan is location at the crossroads of South Asia, Central Asia, and the Middle East makes it an excellent commerce route. Pakistan can benefit greatly from the SCO in terms of economic development as it will help the country to enhance its trade with member states of the SCO, especially the resource-rich Central Asian countries. With its strategic location, the Gwadar Port has the potential to serve as an essential trade route for these nations, promoting trade and stimulating economic growth in the region. Pakistan is an essential hub between the Eurasian region, the Middle East, South Asia, and the Arabian Sea. The governments of the landlocked Central Asian countries have shown a strong interest to utilize Pakistan’s ports of Gwadar and Karachi for connectivity and trade as part of the CPEC. Besides that, Pakistan can profit from the oil and gas resources in Central Asia, which could eventually help the country meet its own energy needs.
Security Cooperation
In terms of security, Pakistan can benefit from the SCO by collaborating on counterterrorism initiatives with other member states through the Regional Anti-Terrorist Structure (RATS) of the organization. Counter Terrorism Military Exercises (CTMEs) are an essential component of the RATS. Pakistan organized a CMTE in 2021, and has attended all CTMEs hosted by SCO countries except the one hosted by India in 2022. Pakistan can share its experiences regarding counterterrorism and intelligence-based operations with the SCO. In exchange, it can gain advantage from cutting-edge intelligence and surveillance technologies of Russia and China.
Pakistan’s Role in SCO
Pakistan has actively participated in the SCO by hosting key events like the Joint Anti-Terrorism Exercise (JATE) in 2021 and the conference on “Transport Connectivity for Regional Prosperity” in November 2023 and “Leveraging Digital Technologies to Enhance Social Safety Nets in SCO Member States” in December 2023. According to the Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Pakistan has scheduled two high-level meetings for 2024 and other meetings under the mandate of SCO Council of Heads of Government. Additionally, in 2025 and 2026, Pakistan will serve as the head of the SCO Council of Regional Antiterrorism Structure (CRATS). Pakistan will assume the rotational Chair of SCO Council of Heads of State (CHS) and SCO Council of Foreign Ministers (CFM) in 2026-2027.
Afghanistan and India
Following the Taliban’s takeover of Afghanistan in 2021, Pakistan has seen an increase in armed attacks. The instability in Afghanistan has led to an increase in violent extremism and terrorism in Pakistan, causing significant challenges, economic harm and widespread human suffering. The Afghan issue has always been high on the organization’s agenda because the national interests and security of member states are linked to the situation in Afghanistan. Thus, SCO is an excellent platform for Pakistan and other member countries to achieve stability in Afghanistan. This is because all countries agree on the importance of a political and diplomatic solution to the problem. Working together through the SCO, these countries can not only assist Afghanistan in achieving stability, but also benefit from a more secure and stable region.
Another challenge for Pakistanis is to handle its complicated relationship with another SCO member i.e. India. Their long-standing antagonism over issues such as Kashmir may impede cooperation inside the organization and cause tension. Both countries need to find ways in order to deal with these issues and focus on areas of shared interest within the SCO framework. In conclusion, the SCO presents Pakistan with an opportunity to deepen its regional integration and foster stronger relationships with other regional countries. By overcoming challenges and seizing opportunities, Pakistan can leverage this platform to enhance economic growth, security cooperation, and overall regional standing.